Intrinsic Rewards
What are intrinsic rewards?
Intrinsic rewards are internal drivers, like personal satisfaction or a sense of purpose, that come from within rather than from external incentives like raises or bonuses.
These rewards are highly personal, as they’re often connected to feelings of pride, a sense of purpose, and fulfillment in one’s work. Employees who experience intrinsic rewards from their professional tasks and activities are more likely to be engaged, productive, and committed.
Characteristics of intrinsic rewards
Some of the main characteristics of intrinsic rewards include:
- Self-generated: They come directly from the individual, driven by personal interests and desires.
- Internally rewarding: Individuals find a sense of personal satisfaction and meaning in performing certain activities.
- Non–monetary: They are not connected to financial benefits or other tangible benefits.
- Professional development: Expanding one’s skills and knowledge through tasks that require effort, critical thinking, or problem-solving is often associated with these kinds of rewards.
- Autonomy-driven: Individuals typically feel a sense of control over their work when they experience intrinsic motivation.

Intrinsic rewards examples
Here are some examples of intrinsic rewards:
- Sense of accomplishment: Feeling pride in one’s work, such as after successfully completing a challenging project or making significant contributions to their team.
- Purpose: When employees feel their work is meaningful, it fosters a strong sense of purpose and direction.
- Personal enjoyment: Experiencing satisfaction while engaging in key activities and tasks.
- Autonomy: Having the freedom to make decisions in your work can provide a feeling of ownership and satisfaction.
- Creativity: Having the freedom to express oneself and contribute innovative ideas provides fulfillment.
- Making progress: Seeing the impact of one’s efforts and knowing those contributions make a difference can enhance motivation.
- Recognition from peers: Receiving praise or appreciation from colleagues can be as rewarding as formal awards or bonuses.
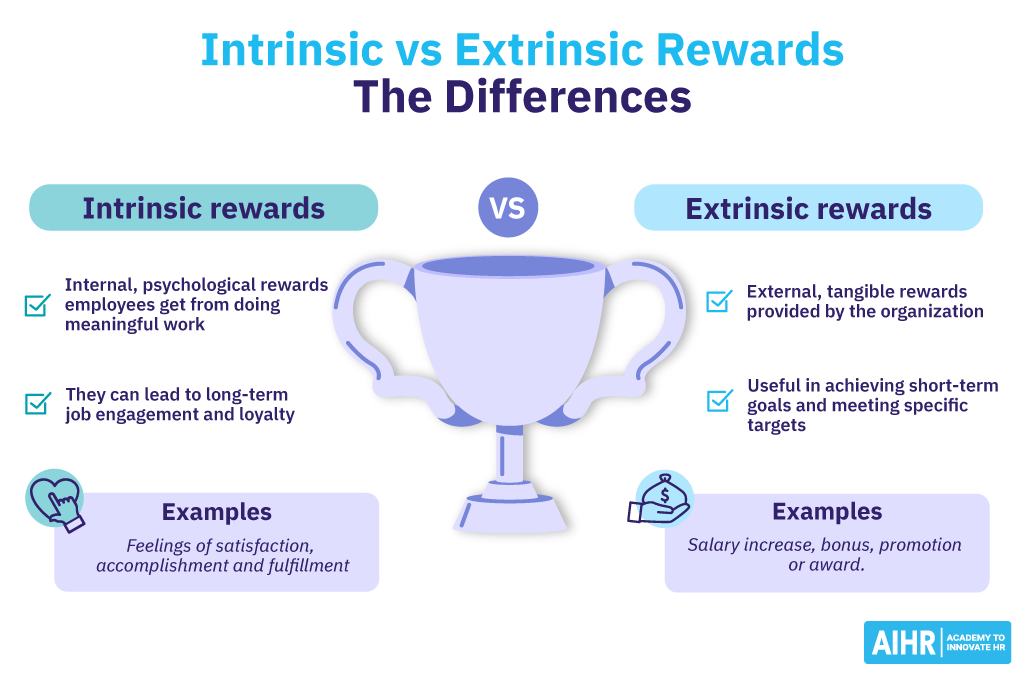
Intrinsic rewards vs. extrinsic rewards
While intrinsic rewards are self-generated motivations that come from within an individual, extrinsic rewards are external incentives employers offer, like raises, bonuses, promotions, or public recognition.
Definition
Internal, personal forms of satisfaction employees derive from performing certain tasks
Tangible, visible rewards (usually with monetary value) employees receive for outstanding performance
Source of motivation
Internal sources, such as personal enjoyment and a sense of purpose
External factors, such as financial compensation or other tangible rewards
Nature
Intangible, never monetary
Tangible, often monetary
Impact
Sustainable, long-lasting
Might lose impact if rewards are not increased
Examples
Sense of achievement, pride, purpose, autonomy
Raises, bonuses, promotions, awards
Why are intrinsic rewards important?
Intrinsic rewards are self-driven and often result from employees’ enjoyment of their work. They can increase engagement, productivity, and overall job satisfaction. They also mean employee motivation is not solely dependent on external factors like monetary rewards or other financial benefits.
Research has shown a direct link between these rewards and high-performance levels. Additionally, Gallup has found that only 33% of U.S. employees (23% globally) feel engaged at work. This greatly impacts business outcomes and organizational success.
By understanding the importance of intrinsic rewards, HR professionals can play a critical role in fostering a work environment where employees feel a sense of purpose, accomplishment, and commitment to their work.
Advantages and disadvantages of intrinsic rewards
Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of fostering intrinsic rewards:
Pros
- Higher retention: Employees who enjoy and feel a strong sense of purpose in their work tend to be more committed and more likely to remain at their company longer.
- Increased innovation: Employees who have a personal investment in their work are more likely to experiment and contribute creative ideas.
- Greater wellbeing: These rewards can improve employees’ overall wellbeing.
- Positive company culture: Prioritizing extrinsic rewards like bonuses or promotions can create an overly competitive company culture. Employees motivated by internal factors, however, are more likely to work collaboratively and create a positive work environment.
Cons
- Difficult to measure: Because these rewards are highly personal and dependent on internal motivations, their impact on employee performance and organizational success can be difficult to measure.
- Not universally effective: Intrinsic rewards may not motivate everyone sufficiently. Depending on the industry, company culture, and personal preferences, internal motivation may be difficult to generate and sustain.
- Takes time to develop: Internal sources of motivation, purpose, and fulfillment often depend on one’s role. Developing intrinsic rewards may require sustained effort, which can take some time.
- Limited control: While organizations can control the types of external rewards they provide, creating the right environment and tasks to drive intrinsic motivation is difficult as not everyone has the same motivations.
- Lack of understanding: Some managers may not fully understand intrinsic rewards’ positive impact on employee performance and engagement, resulting in excessive reliance on tangible, monetary awards.
Using intrinsic rewards in the workplace: 6 tips for HR
What role can HR professionals play in supporting employees to develop intrinsic rewards? Here are some helpful tips:
- Create a culture of continuous feedback: Employees who receive regular feedback and understand how their contributions impact team and organizational success tend to feel noticed, valued, and motivated.
- Celebrate achievements: Establish peer recognition programs where employees can recognize each other’s contributions. Mutual recognition typically results in mutual motivation.
- Promote autonomy: Develop a work culture where employees feel a sense of control over their work, such as the ability to set personal and professional goals, manage their time effectively, and have greater choice over how they get their work done (e.g., flexible work options).
- Align individual values with professional goals: Work with managers to incorporate employees’ individual values (e.g., interest in sustainability, desire for greater work-life balance, etc.) into professional development plans.
- Provide professional growth opportunities: Invest in initiatives like training programs, mentoring and coaching, and professional development plans to motivate employees to improve their skills and advance their careers. This can drive their sense of achievement and job satisfaction, which increases intrinsic motivation.
- Monitor and evaluate impact: To ensure initiatives to inspire intrinsic rewards are effective, track their impact through employee surveys, performance discussions and reviews, and other performance metrics. This can help you identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
HR tip
Since intrinsic rewards are highly personal, they support managers in identifying and understanding individual team members’ internal motivators. Together, you can develop plans, training initiatives, or mentoring/coaching opportunities to drive team engagement, productivity, and performance. Help managers to determine which internal motivators align with organizational goals in order to drive business outcomes and create a more fulfilling work environment.
FAQ
Intrinsic rewards are internal motivators employees experience by doing certain tasks and activities. Common examples of these kinds of rewards include a sense of pride, purpose, and accomplishment in one’s work.
While intrinsic rewards are internal, self-generated motivations that come from within an individual, extrinsic rewards come in the form of external incentives like raises, bonuses, or promotions.