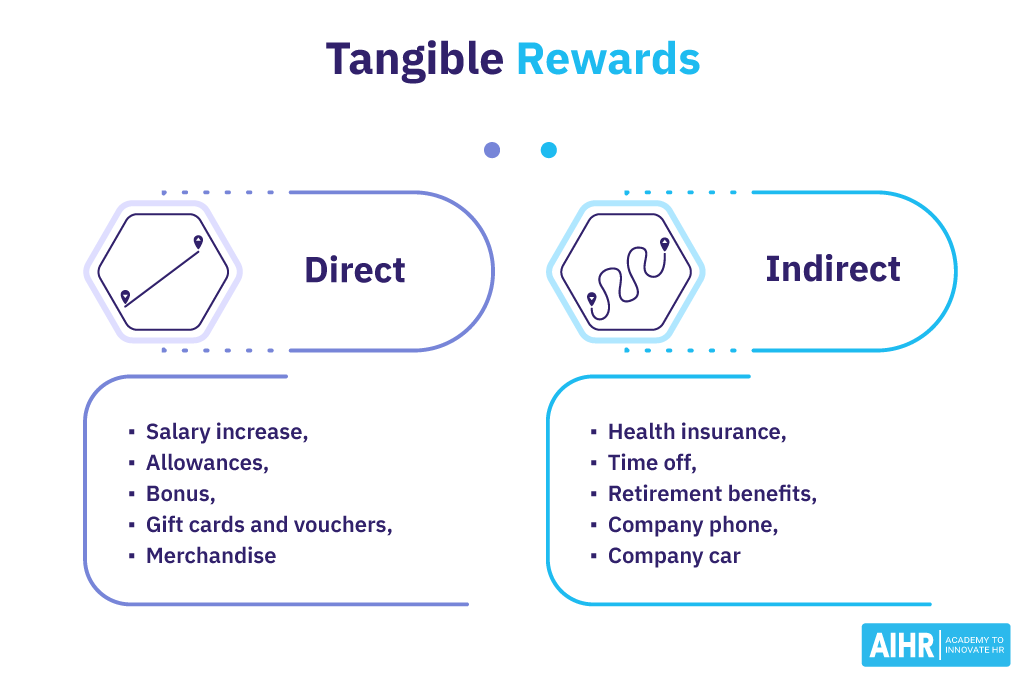
Tangible Rewards
What are tangible rewards?
Tangible rewards are incentives used to recognize and appreciate employees’ contributions. They can be cash-based, such as bonuses, or non-cash rewards with a clear monetary value, like gift cards or company perks.
Beyond financial benefits, tangible rewards can boost morale and encourage discretionary effort. For example, if an employee receives a cash bonus for assisting a high-value customer in a challenging situation, they are more likely to repeat that behavior in the future. When employees feel appropriately rewarded, they tend to stay motivated, take more initiative, and even demonstrate increased creativity in their roles.
Tangible rewards are also highly preferred by employees — 62% say they would rather receive tangible incentives (even small ones) over recognition or other intangible rewards. This highlights the importance of offering meaningful, concrete rewards rather than relying solely on verbal praise or symbolic gestures.
Tangible rewards examples
Here are some examples of tangible rewards for employees:
- Salary increase: A fixed reward that increases the employee’s regular wage or salary.
- Bonus: Awarded in the form of cash, either annually or as a one-time payment.
- Gift card: A gift card or voucher tailored to suit the employee’s preference or interests might be useful.
- Profit sharing: A portion of company profits is distributed to employees.
- Company-branded merchandise: This could be a company hoodie, laptop, notebook, or other branded items.
- Company perks: This could include free meals, gym memberships, or transportation allowances.
- Wellness incentives: Discounts on fitness programs, health insurance premium reductions, or other health-related benefits.
- Employee discounts: Special pricing offered exclusively to employees on company products or services.
- Tuition reimbursement: Financial assistance for further education, professional certifications, or training programs.
- Paid time off (PTO) rewards: Additional vacation or personal days.
Learn how to design a Total Rewards Strategy
Determining which tangible rewards your organization will offer is one of your considerations when developing a Total Rewards Strategy.
In AIHR’s Compensation and Benefits Certificate Program you will learn how to create a compensation & benefits strategy by analyzing internal and external factors to develop right strategy for your company.
This online, self-paced program will teach you q holistic approach to rewards, from direct cash and core benefits to wellbeing and recognition.
Tangible vs. intangible rewards
Tangible and intangible rewards are both used to motivate and recognize employees, but they differ in their form and impact.
Definition
Physical or financial incentives with measurable value.
Non-material incentives that enhance motivation and job satisfaction.
Examples
Salary increases, bonuses, gift cards, stock options, company perks.
Recognition, praise, career development, flexible work arrangements.
Monetary value
Has a direct financial or material value.
No direct monetary value but contributes to engagement and satisfaction.
Customization
Often standardized, based on company policies.
Can be personalized to suit employees’ preferences.
Advantages and disadvantages of tangible rewards
Tangible rewards form a significant part of any successful compensation strategy for an organization. Some of their benefits include:
- Clear value: Monetary or material rewards have a concrete, easily understood worth.
- Competitive advantage: Offering strong tangible benefits can help attract and retain top talent.
- Encourages performance-driven culture: Employees are likely to work harder when rewards are directly tied to results.
- Flexibility in options: Employers can tailor tangible incentives to different needs, such as financial incentives, perks, or merchandise.
HR tip
Combine tangible and intangible rewards for greater impact.
Tangible benefits are most effective when paired with meaningful recognition. For instance, a cash bonus will feel more valuable if accompanied by public praise from leadership. Acknowledging employees in company-wide meetings or through personalized “thank you” notes adds an extra layer of recognition, reinforcing their contributions.
Not every employee will receive a tangible reward at the same time, or even at all. As a result, the following negative repercussions can occur:
- Short-term motivation: Employees may focus on the reward rather than long-term engagement or job satisfaction.
- Can become expected: Over time, tangible rewards may be seen as entitlements rather than incentives.
- Costly for employees: Financial incentives, perks, and bonuses can be expensive, especially for large workforces.
- May create unhealthy competition: Employees might prioritize rewards over teamwork, leading to conflicts or decreased collaboration.
How to provide tangible rewards effectively
Here’s how HR professionals can provide tangible rewards effectively:
- Align rewards with business objectives: Ensure tangible incentives are tied to company goals, performance metrics, and HR strategies to reinforce desired behaviors.
- Offer meaningful and flexible rewards: Employees have different needs, so providing options like bonuses, additional PTO, or professional development stipends makes rewards more impactful.
- Balance short-term and long-term incentives: To encourage engagement, use a mix of immediate recognition (e.g., spot bonuses) and long-term benefits (e.g., stock options, retention bonuses).
- Be consistent and transparent: Establish clear criteria for earning rewards, so employees understand how their performance relates to incentives.
- Personalize rewards where possible: Use employee feedback or HR data to offer relevant perks, such as childcare stipends, wellness incentives, or remote work support.
- Continuously evaluate and improve: Regularly review reward programs through employee feedback, engagement surveys, and HR analytics to ensure effectiveness.