Extrinsic Rewards
What are extrinsic rewards?
Extrinsic rewards are external incentives employees receive as encouragement or compensation for completing a task or achieving certain goals. They are often, but not always, financial in nature.

Extrinsic rewards examples
Some common examples of extrinsic rewards in the workplace are:
- Bonuses: Additional financial compensation based on individual, team, or company performance.
- Salary increases: Incremental raises in an employee’s base pay.
- Promotions: Advancing to a higher position with increased responsibilities and pay.
- Commissions: Earnings given to sales employees based on the amount of sales they generate.
- Gift cards: Vouchers for specific amounts to be spent at certain retailers or restaurants.
- Paid time off: Additional vacation days or paid leave as a reward for exceptional performance.
- Tangible prizes: Items such as electronics, gadgets, or other merchandise given as rewards.
- Employee-of-the-month awards: Recognition programs that often include a certificate, plaque, or additional perks.
- Stock options: Opportunities for employees to purchase company shares at a discounted price.
- Recognition and praise: Public acknowledgment of an employee’s efforts and achievements.
Intrinsic vs. extrinsic rewards
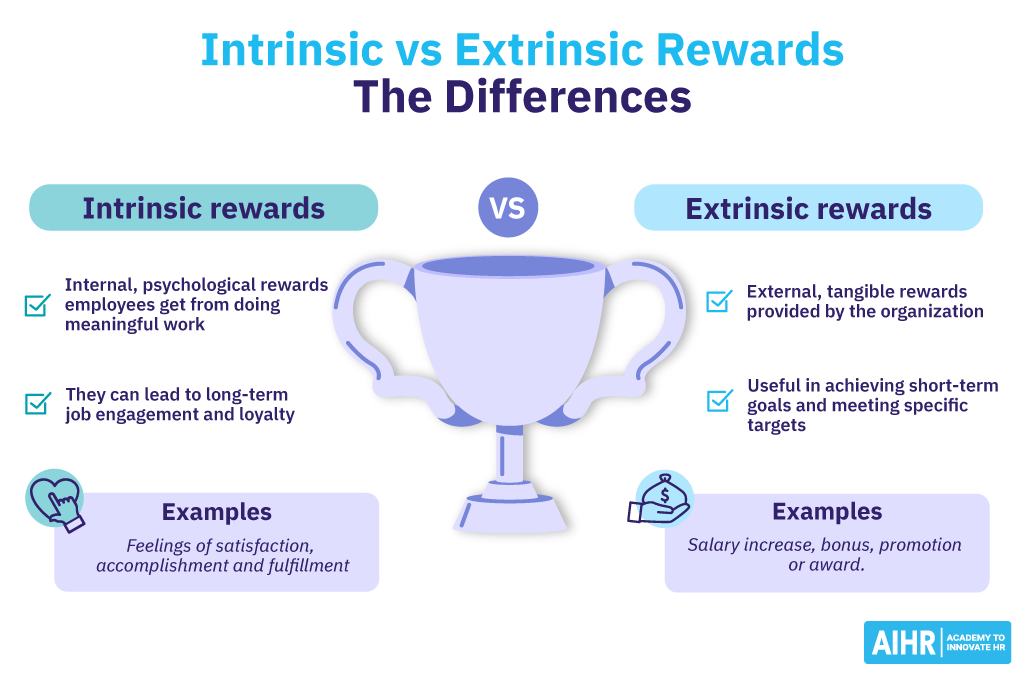
Intrinsic rewards are internal, psychological rewards that employees get from doing meaningful work. They are self-administered and involve feelings of satisfaction, accomplishment, and fulfillment. On the other hand, extrinsic rewards are external incentives the organization provides. They include tangible benefits like salary increases, bonuses, promotions, or awards, as well as social recognition like employee-of-the-month programs. Some of their key differences are:
- Nature of the reward: Extrinsic rewards originate from external sources, such as compensation, bonuses, and awards. Intrinsic rewards, like satisfaction or feelings of achievement, originate internally from an employee’s job satisfaction.
- Source of motivation: Extrinsic rewards motivate employees through external factors, pushing them to excel in order to obtain these rewards. In contrast, intrinsic rewards are driven by internal aspirations, such as the personal satisfaction derived from performing their job well.
- Impact on performance: Extrinsic rewards can boost short-term performance but risk undermining long-term motivation if over-relied on. Intrinsic rewards are linked to long-term positive effects on performance, motivation, and job satisfaction.
The importance of extrinsic rewards
Extrinsic rewards play a crucial role in motivating employees and shaping their behavior. They act as tangible recognitions of an individual’s efforts and achievements, making them feel valued and appreciated.
One key reason these rewards are important is they can align individual goals with organizational objectives. By rewarding behaviors and outcomes that contribute to the company’s success, employers can guide their workforce toward desired results. This is especially effective in large organizations, where personal motivations might not always align with company goals.
Extrinsic rewards can also help attract and retain talent by making the company more appealing to potential employees. Additionally, these rewards can help retain top performers who might otherwise seek opportunities elsewhere.
Advantages and disadvantages of extrinsic rewards
There are advantages and disadvantages to utilizing extrinsic rewards within an organization.
Pros
- Extrinsic rewards can provide immediate motivation to complete a task or achieve a goal. For instance, bonuses can motivate employees to reach their targets
- They can enhance performance, especially for straightforward, routine tasks where the path to the goal is clear
- Extrinsic rewards such as bonuses or awards are straightforward to implement and understand
- They show the organization values its employees and their efforts, which can help improve commitment to the company.
Cons
- Over time, the effectiveness of these rewards can diminish, requiring greater incentives to achieve the same level of motivation
- If not managed properly, extrinsic rewards can create unhealthy competition, envy, or feelings of unfairness among employees
- Employees may come to believe they should always receive a reward for certain types of behavior or for reaching certain goals, which means they may not be motivated in areas without them
- Relying heavily on these rewards can undermine intrinsic motivation – the internal desire to perform a task for its own sake.
Using extrinsic rewards in the workplace: Tips for HR
If you’re planning to use an extrinsic reward structure in your workplace, there are several tips to keep in mind:
- Clearly define your rewards and the criteria for earning them: Employees should understand what is expected of them and what they can do to earn these rewards.
- Align the rewards system with organizational goals: Ensure the rewards offered are in line with company objectives. For instance, if teamwork is a priority, rewards should be structured to promote and recognize collaborative efforts.
- Offer a variety of rewards, including non-monetary incentives: Not all employees are motivated by the same things. Tailor and personalize rewards where possible to resonate better with employees.
- Ensure fairness and transparency: Apply the rewards system consistently across all departments and levels. Inconsistency can lead to perceptions of favoritism and reduced employee motivation.
- Balance extrinsic and intrinsic rewards: While extrinsic rewards are effective, they work best when combined with intrinsic motivators like meaningful work, growth opportunities, and a positive workplace culture.
- Review and update the rewards system regularly: As the company evolves, so should its reward system. Regularly assess the effectiveness of the rewards and make adjustments as needed. This also keeps the program fresh and engaging.
FAQ
An example of an extrinsic reward is a bonus or financial incentive given to an employee for meeting or exceeding performance targets. This reward is external to the individual and serves as a motivation for achieving specific goals.
Extrinsic rewards are external incentives like bonuses, promotions, or praise used to motivate employees. Intrinsic rewards come from internal satisfaction, such as a sense of achievement or personal growth, that comes from professional tasks and achievements.