Self Managed Teams
What are self managed teams?
A self managed team, also known as a self organized team, is a group of individuals responsible for organizing and handling their work without a traditional hierarchical structure or external direction. Members of a self managed work team empower themselves to make decisions and solve problems with the support and trust of the team and company.
How do self managed teams work?
In practice, self managed teams work by distributing leadership and responsibility among team members rather than relying on a single manager. This setup encourages collaboration, shared accountability, and empowerment. Team members typically rotate roles or take on duties that suit their skills, and they collectively handle issues like performance reviews or problem-solving.
These teams often thrive when they have clear goals, open communication, and mutual trust. While they can improve productivity and employee satisfaction, they also require team members to be highly motivated, organized, and skilled in managing both their work and team dynamics.
The characteristics of self managed teams
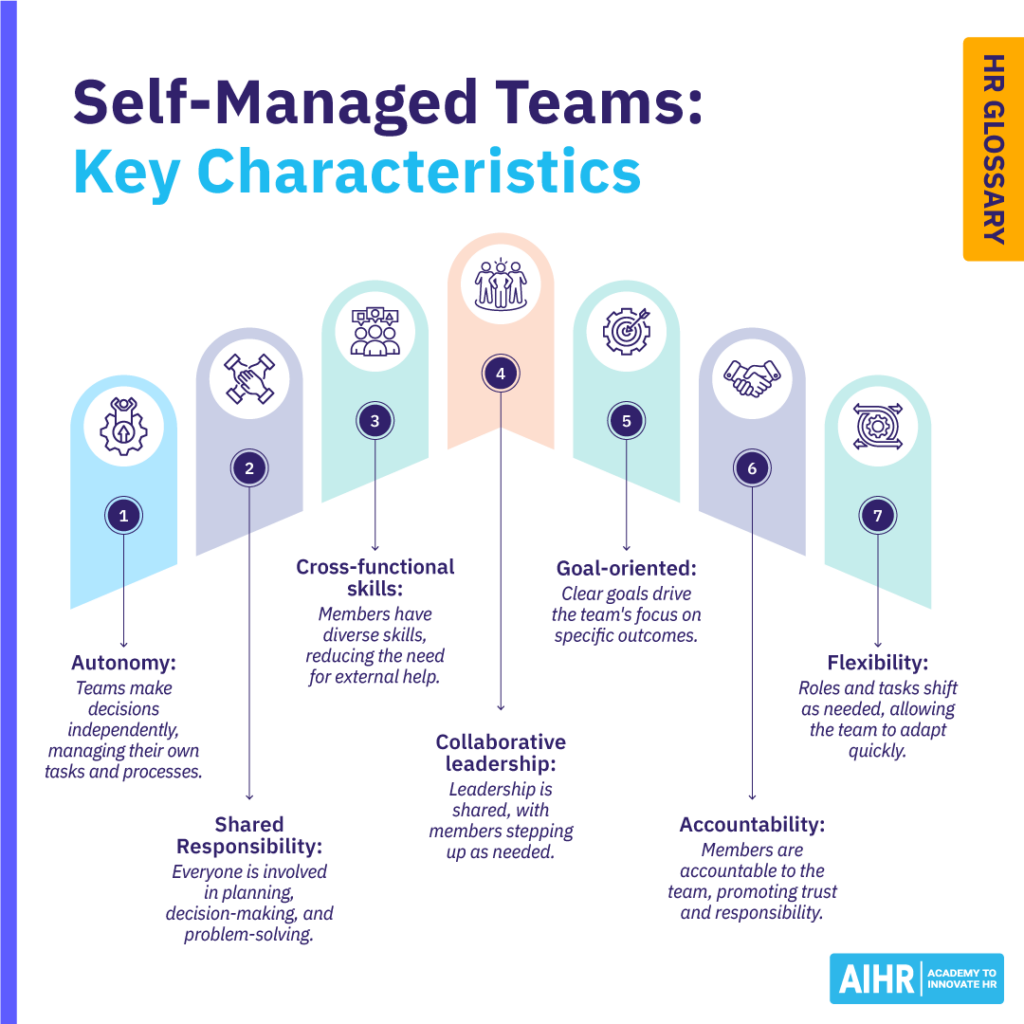
Self managed work teams have several key characteristics that make them distinct:
- Autonomy: Team members have the authority to make decisions without needing approval from higher management, allowing them to manage their own tasks and processes.
- Shared responsibility: The team collectively takes responsibility for their outcomes, including planning, decision-making, and problem-solving.
- Cross-functional skills: Members often possess diverse skill sets, enabling the team to handle a variety of tasks without external support.
- Collaborative leadership: Rather than having a single leader, leadership is distributed across the team, with individuals stepping up based on expertise or the needs of the moment.
- Goal-oriented: Teams are usually focused on specific outcomes or deliverables, with clear goals and a shared commitment to achieving them.
- Accountability: Each member is accountable to the entire team, fostering a culture of mutual trust and responsibility.
- Flexibility: Team roles and responsibilities can shift based on project needs, allowing the group to adapt quickly to changes or challenges.
Examples of self managed teams
One example of a self managed work team is the team responsible for developing and maintaining the Linux operating system. Linux is an open-source project, meaning anyone can contribute to the software’s advancement and improvement. The team comprises volunteers and professionals worldwide who collaborate and coordinate their efforts through online communication and collaboration tools.
Some other examples of businesses that use this team structure include:
- Zappos: Zappos’ use of a flat organizational structure (holacracy) empowers employees to make decisions independently, aligning well with the self managed team concept.
- W.L. Gore & Associates: Known for its decentralized structure, W.L. Gore encourages employees to take ownership of their work, making decisions without heavy managerial oversight—another hallmark of self-management.
- Valve Corporation: Valve’s structure gives employees the freedom to choose projects and work autonomously with little oversight from management, which perfectly fits the description of a self managed team.
Traditional team vs. self managed team
Here’s a quick comparison between traditional teams and self managed teams:
Leadership
Led by a manager or team leader
Leadership is shared or rotated among members
Responsibility
Manager assigns tasks and monitors progress
Team is responsible for planning, organizing, and executing tasks
Skill specialization
Typically specialized roles
Cross-functional skills within the team
Goal-setting
Goals set by the manager or leadership
Team sets its own goals collaboratively
Adaptability
Limited flexibility; relies on manager’s direction
High flexibility; team adapts to changes independently
Advantages and disadvantages of self managed teams
The advantages
Some of the key advantages include the following:
- Increased flexibility: They can be more flexible and adaptable than traditional hierarchical teams. Because team members are independent and responsible for organizing and managing their work, they can quickly respond to changing priorities and opportunities. This reaction can be beneficial in fast-paced or uncertain environments where organizations must adapt and innovate.
- Increased collaboration: They can foster a culture of collaboration and inclusiveness, where all members can contribute their ideas. This way of business can lead to better decision-making and problem-solving and boost trust among team members.
- Increased accountability: They can promote a sense of ownership and responsibility among team members. When team members are allowed to take ownership of their work, they are likely to feel invested in the triumphs of the team and the organization. This empowerment can drive better performance and results.
The disadvantages
Some potential drawbacks include the following:
- Lack of clear direction: Without a designated leader, these teams may struggle to set clear goals and direction, leading to confusion and a lack of focus.
- Conflict and disagreement: They can also be more prone to conflict and discord. Because team members can make decisions, there may be more opportunities for contradictory ideas and perspectives. This clashing can lead to tension, frustration, and dysfunctional conflict within the team if not properly managed.
- Dependence on collaboration and communication: They rely heavily on teamwork and communication to succeed. Team members need to be able to cooperate effectively and communicate to ensure the team can achieve its pursuits.
Learn the skills to effectively lead self managed teams
Effectively leading self managed teams is essential for HR professionals aiming to foster collaboration, autonomy, and accountability within their organizations.
In AIHR’s HR Manager Certificate Program, you will learn the strategies and skills needed to empower self managed teams, streamline team dynamics, and enhance performance.
This online, self-paced Certificate Program will also provide practical insights into managing team autonomy, resolving conflicts, and aligning team goals with broader business objectives.
How to implement self managed teams
If an organization is considering implementing self managed teams, several key steps can help ensure a successful transition:
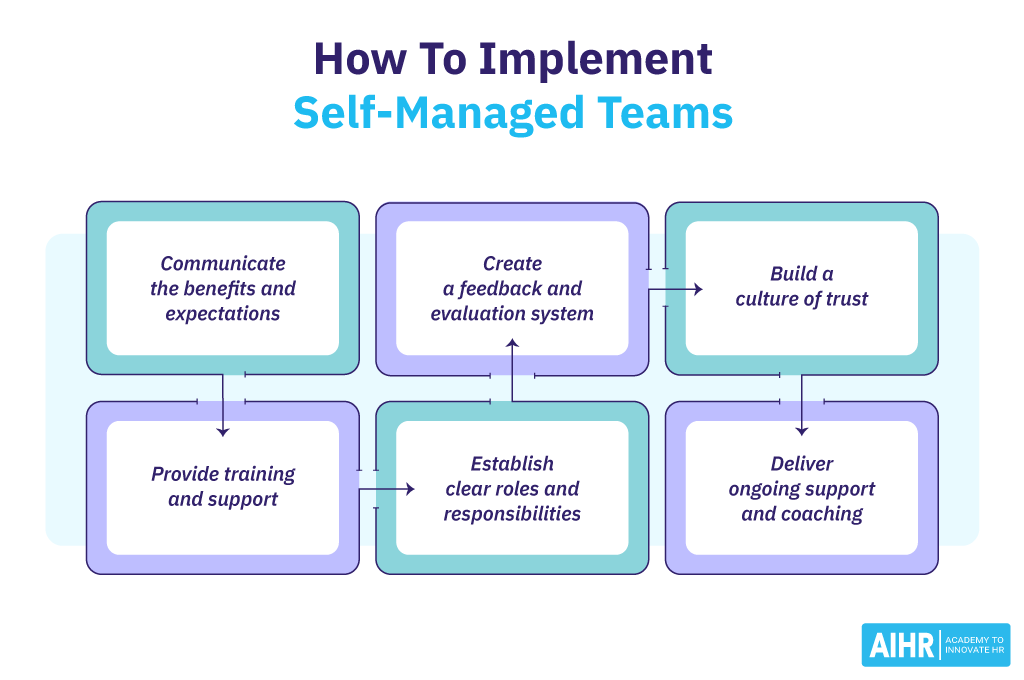
- Step 1: Communicate the benefits and expectations to all stakeholders, including team members and leadership.
- Step 2: Provide training and support for team members to develop necessary skills, such as conflict resolution, decision-making, and communication.
- Step 3: Establish clear roles and responsibilities for team members, including how they collaborate and make decisions.
- Step 4: Create a feedback and evaluation system to regularly assess the team’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Step 5: Build a culture of trust where team members feel comfortable taking ownership and accountability for their work.
- Step 6: Deliver ongoing support and coaching to help the team succeed and continue to grow and develop.
HR tip
When implementing self managed teams, ensure members have clear goals, strong communication skills, and access to the right resources. Providing initial training on decision-making and conflict resolution can help them thrive in their new autonomous roles.
FAQ
Self managed teams are groups of employees who operate without direct supervision. They have the autonomy to make decisions related to their tasks, roles, and processes. These teams are typically responsible for planning, organizing, and controlling their work to achieve set goals.
Self managed teams typically don’t have a traditional leader. Instead, leadership responsibilities are often shared among team members. However, some teams may have a facilitator or coordinator who helps guide the group without exercising direct authority.
The key difference is in the level of autonomy. Self managed teams have some control over how they complete tasks but often work within goals and guidelines set by management. Self directed teams have full autonomy, including deciding their goals, tasks, and how to achieve them, with little to no outside direction.