Decentralized Organizational Structure
What is a decentralized organizational structure?
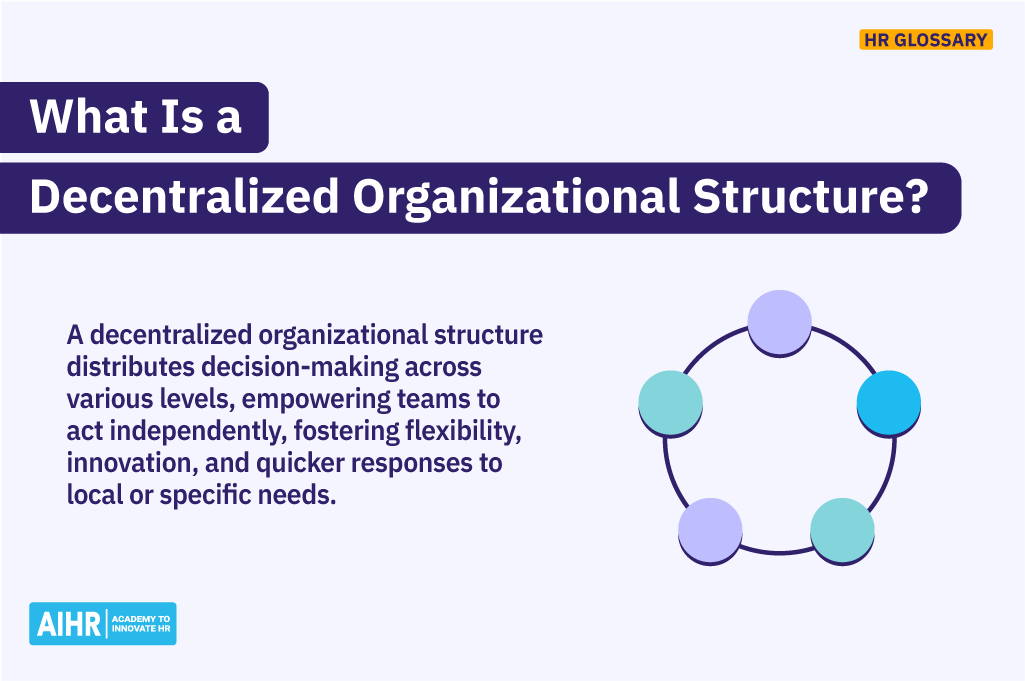
A decentralized organizational structure is a type of organizational design framework in which decision-making authority is distributed throughout the organization rather than concentrated at the top. This often means mid- and lower-level managers can make decisions that affect their teams and projects without prior approval from senior management.
One of the main benefits of a decentralized organizational structure is that it allows senior leaders to focus on more strategic tasks rather than on daily decision-making.
Some companies that have a decentralized organizational structure are:
- Johnson & Johnson: Known for its autonomous business units, Johnson & Johnson operates as a collection of over 250 companies worldwide. Each unit has significant decision-making authority, allowing them to innovate and respond quickly to local market needs.
- Coca-Cola: While the company’s brand guidelines are globally consistent, its regional teams have the flexibility to make decisions about product offerings, distribution strategies, and marketing campaigns.
Characteristics of a decentralized organizational structure
A decentralized organizational structure differs greatly from traditional organizational structures with a top-down approach. Here are some characteristics of a decentralized organization:
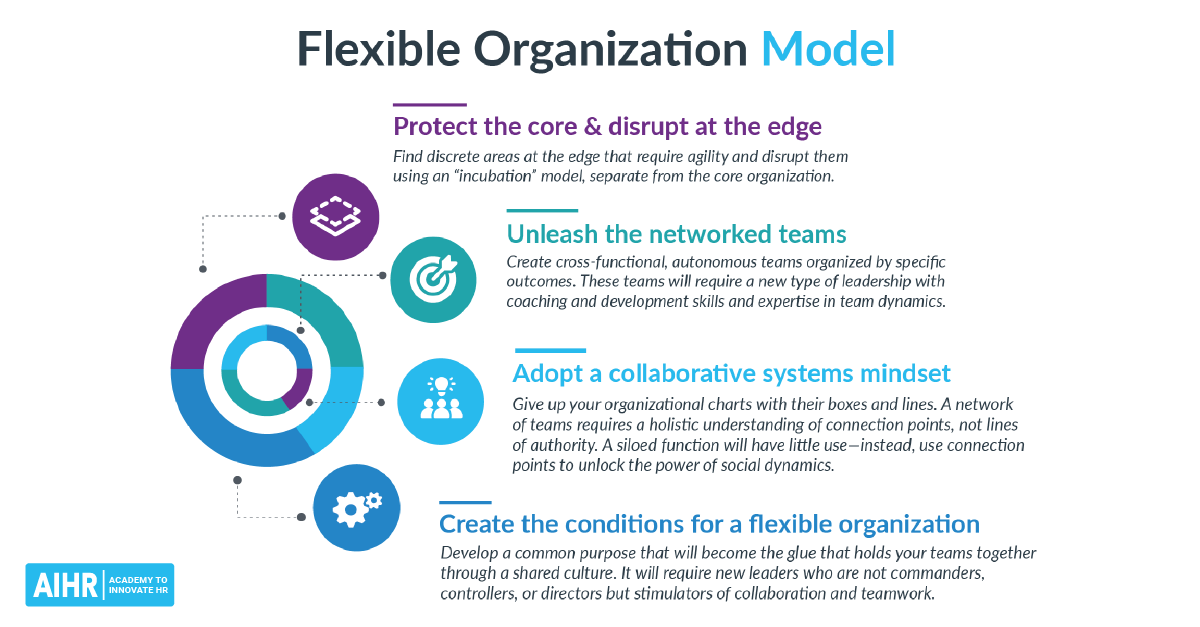
- Distributed decision-making: Rather than most decisions coming from senior leadership, managers and teams have decision-making power over their key tasks and projects.
- Cross–functional teams: Work is typically structured around self-managing cross-functional teams responsible for driving projects.
- Increased agility: Employees have more autonomy to make their own decisions, which means they can respond and make changes more quickly.
- Encourages innovation: Employees usually have the freedom to act upon creative ideas without waiting for approval, enabling quick application of innovative insights.
- Reduced burden on top management: By distributing decision-making, top leaders don’t have to worry about every operational decision, allowing them to focus on strategic planning.
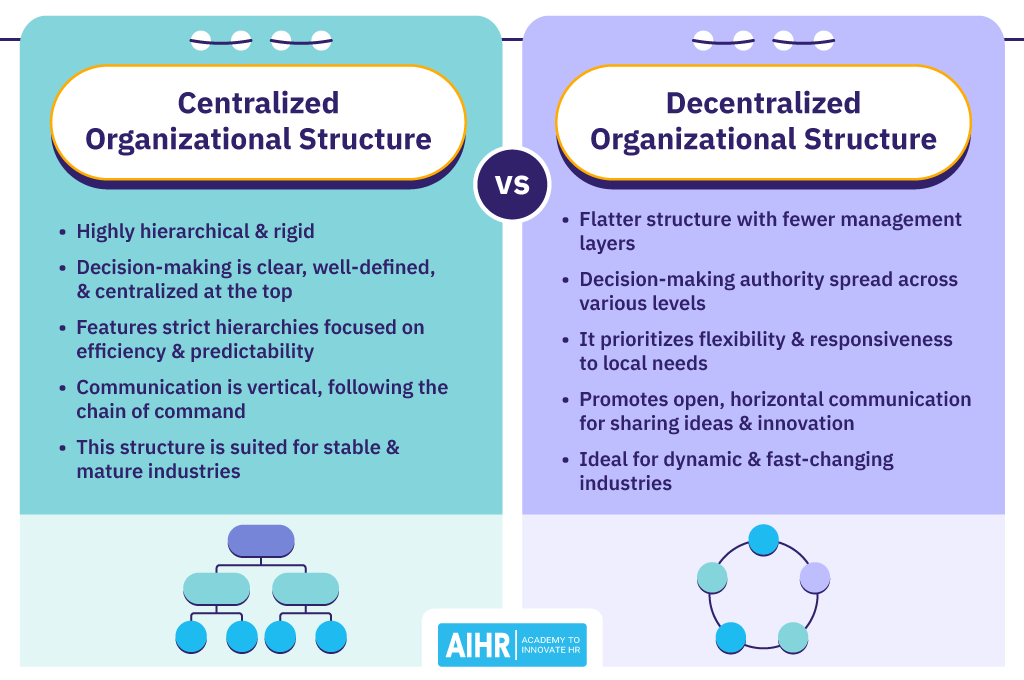
Centralized vs. decentralized organizational structure
Hierarchy
Multiple management layers
Flatter structure with fewer management layers
Employee autonomy
Limited; senior leaders make the majority of key decisions
Increased control; employees are able to make decisions
Productivity
Can be less productive if employees often have to wait for approval from senior management
Increased productivity within self-directed teams due to the ability to make decisions without constant approval processes
Communication
Typically top-down
More open and transparent
Types of roles
Specialized, structured, and standardized roles and responsibilities
More fluid and adaptable
Decentralized organizational structure example
Here is an example of how a decentralized organizational structure might work:
OptiLearn, an AI-driven company specializing in upskilling and reskilling employees, operates through decentralized hubs in North America, Europe, and Asia. This structure allows each regional office to tailor its learning solutions to meet local demands under the leadership of regional managers, fostering innovation and responsiveness to market needs.
Key functions, such as data security, are centralized at its headquarters in San Francisco, ensuring consistency in critical operational areas. OptiLearn’s senior management team is tasked with strategic planning, focusing on expanding into emerging markets and enhancing the scalability of their platforms.
This hybrid approach combines the flexibility of decentralized decision-making with centralized oversight, enabling OptiLearn to adapt efficiently to global trends while maintaining high standards in data security and strategic growth. This ensures its continued competitiveness in the educational technology sector.
Enhance organizational agility with a decentralized structure
Decentralized organizational structure advantages and disadvantages
Here are some of the benefits of a decentralized organizational structure:
- Faster decision-making: Decentralization allows decisions to be made closer to the point of action, leading to quicker responses to market changes, customer needs, and operational challenges.
- Encouraging leadership skills: Decentralization gives managers at various levels the opportunity to exercise their judgment and decision-making skills, which can help develop future leaders within the organization.
- Boosts employee engagement: Managers, team leaders, and individual employees often benefit from working in an environment where senior leaders trust them to manage tasks and make decisions without needing constant approval.
- Strategic focus: When senior leaders don’t have to be involved in daily decision-making, they have more time to focus on strategic goals and other long-term objectives.
Drawbacks of this organizational structure include:
- Not suitable for all industries: A decentralized organizational structure may not work as well in some types of organizations. For example, highly regulated industries such as healthcare, pharmaceuticals, finance, or new companies need centralized decision-making processes to ensure minimal errors.
- Risk of effort duplication: A lack of central oversight may lead to different managers and teams working on similar tasks or projects. This inefficiency can impact productivity and waste time and resources.
- Potential for inconsistency: With more people making decisions, there’s a risk of inconsistencies and lack of uniformity in practices and policies, which can confuse employees and customers.
- Dilution of company culture: Maintaining a consistent and unified culture can be more challenging when decision-making power is spread across different teams. This lack of unity can potentially dilute a company’s mission and values.
Implementing a decentralized organizational structure: Tips for HR
How can HR help drive the successful implantation of a decentralized organizational culture? Follow these tips:
- Build training programs: Both managers and employees will need support building the necessary skills and knowledge to make decisions independently. Key focus areas for training include leadership skills, critical thinking, effective communication and collaboration, and problem-solving.
- Encourage ongoing feedback: Promote a culture of regular feedback through comprehensive continuous performance management systems. Encourage managers and employees to conduct periodic reviews to discuss goals and performance, ensuring they align with company objectives.
- Support leadership development: Identify managers and individual team members who consistently deliver results through well-informed decisions. Invest in leadership development to support their continued career growth.
- Develop clear performance metrics: Establish clear metrics to monitor and track performance to hold managers and teams accountable for decision-making authority. Ensure employees understand the criteria upon which they will be assessed and identify areas for improvement and further development.
- Ensure transparent communication channels: Establishing clear, consistent communication channels is essential to prevent inefficient duplication of efforts in cross-functional teams. Ensure employees can easily access knowledge-sharing platforms to keep them updated on critical projects, company changes, and other relevant information.
FAQ
A decentralized organizational structure is an organizational design framework that distributes decision-making authority across various levels rather than concentrating it at the top. This allows teams and individuals closer to specific tasks or markets to make decisions independently, fostering quicker responses, innovation, and flexibility.
An example of a decentralized organization is a university system with multiple campuses, where each campus independently manages its budget, curriculum, and operations, while a central board oversees overall policies and goals.
The main reason for decentralization is to enable faster decision-making and greater flexibility by distributing authority to lower levels of an organization, allowing those closer to specific tasks or challenges to respond more effectively.