Emotional Compensation
What is emotional compensation?
Emotional compensation, also known as emotional salary, refers to the non-monetary incentives and benefits that positively impact employees’ wellbeing and satisfaction in the workplace. It includes factors employees value, like recognition, autonomy, belonging, personal growth, and meaningful work.
In addition to base pay, many organizations implement various emotional compensation initiatives, such as employee recognition programs, flexible work arrangements, wellness programs, and social activities.
Emotional compensation benefits both employees and organizations, as it can increase employee motivation, engagement, and commitment.
Examples of emotional compensation
Some common examples of emotional compensation include:
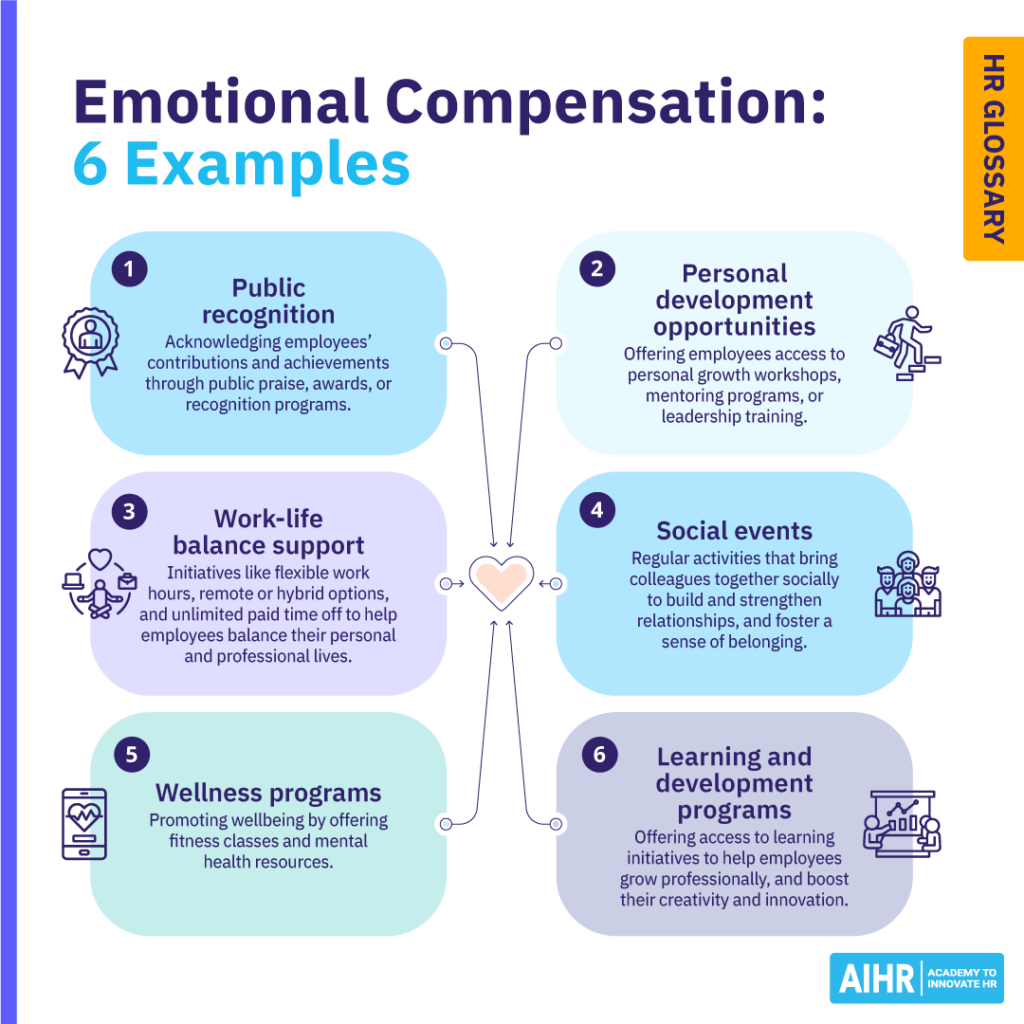
- Public recognition: Acknowledging employees’ contributions and achievements through public praise, awards, recognition programs, or simple expressions of gratitude can make employees feel valued and appreciated.
- Personal development opportunities: Offering employees access to personal growth workshops, mentoring programs, or leadership training helps them feel emotionally supported and invested in the company.
- Work-life balance support: Initiatives like flexible work hours, remote or hybrid work options, or unlimited paid time off can help employees balance their personal lives and improve their overall wellbeing.
- Social events: Regular activities that bring colleagues together socially can build and strengthen relationships, improve connections, and foster a sense of belonging in the workplace.
- Wellness programs: Promoting wellbeing by offering fitness classes and mental wellness resources can positively impact employees’ physical and mental health.
- Learning and development programs: Most employees want opportunities to learn more and further develop their skills. Offering access to learning initiatives (e.g., microlearning modules, online courses, workshops, and professional growth resources) can help employees grow professionally and boost their creativity and innovation.
The importance of emotional compensation
Although financial rewards are important, employees desire more from their employers. Overall, they look for workplaces that offer good pay and where they feel respected, valued, and connected to others. Emotional compensation addresses these needs by enhancing the quality of the work environment through various supportive initiatives.
Organizations that invest in employees’ psychological and emotional wellbeing have a significant advantage in a competitive job market. Initiatives that contribute to emotional compensation—like recognition programs, personal development opportunities, and efforts to foster social connections among staff—make employees feel appreciated and integral to the organization. This is crucial because when employees feel their emotional and professional needs are met, they are more likely to stay with a company, reducing turnover and the costs associated with recruiting and training new hires.
Furthermore, emotionally compensated employees are often more motivated and engaged. They will likely invest more in their roles, drive innovation, and push the company forward.
The benefits of offering emotional compensation
Providing emotional compensation comes with the following benefits to both employees and the organization:
- Improved employee morale: Recognizing and valuing employees’ emotional needs can boost morale and create a positive work atmosphere.
- Increased retention: People tend to stay longer with organizations that make them feel valued and supported, thereby increasing the employee retention rate.
- Greater productivity: Feeling emotionally supported at work can help employees feel more invested in their work, improving overall productivity.
- Stronger workplace relationships: When organizations emphasize the importance of building relationships in the workplace, it can lead to better collaboration and relationships among team members.
- Better mental health: Receiving emotional support at work can reduce stress and anxiety, which can lower the absenteeism rate and risk of burnout.
HR tip
To highlight the positive impact of emotional compensation, regularly share success stories from employees who have benefited from company initiatives. Use different communication channels, from internal newsletters and employee forums to online collaboration platforms. Consider using positive employee testimonials in recruitment channels to attract and retain talent.
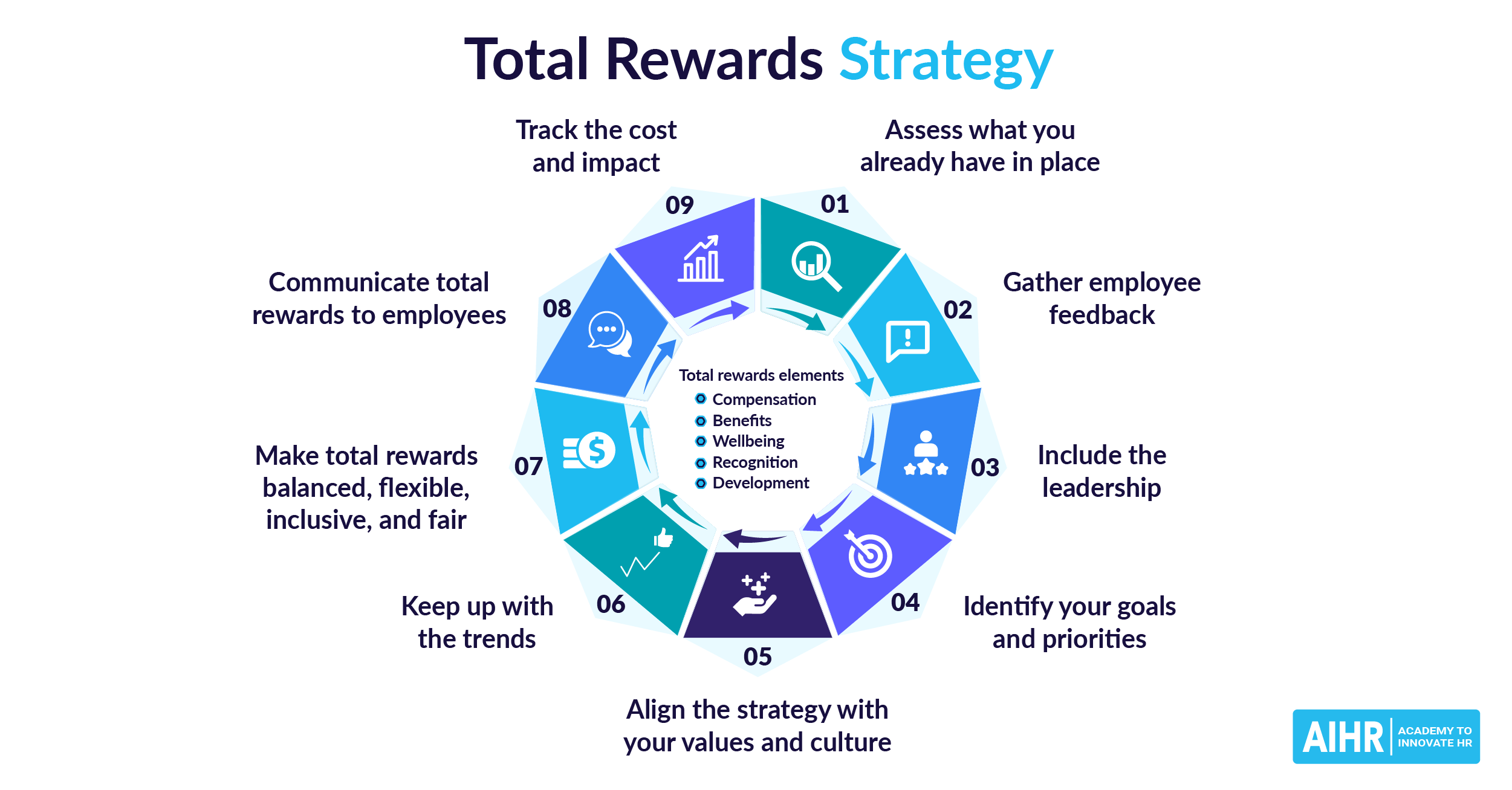
How to implement an emotional compensation strategy
By following these simple steps, you can successfully implement an emotional compensation strategy:
Step 1: Get employee input
Find out firsthand what kind of emotional compensation benefits they desire most. You can conduct an online survey to determine company-wide initiatives or encourage managers to regularly check in with team members to understand individual needs and personal preferences.
Step 2: Set clear objectives
Use employee input, along with other key metrics, to set overall goals. These can include increasing job satisfaction, engagement, and productivity. Then, determine how best to achieve those goals, setting timelines and realistic expectations to ensure you can fulfill your objectives.
Step 3: Determine the budget
Prioritize the most critical emotional compensation initiatives that align employee needs and organizational goals, then set the budget and allocate the necessary resources to them. This will help you and your HR team ensure that the most important and urgent objectives are met on time.
Step 4: Roll out and communicate the initiatives
Make sure all employees and prospective candidates know about the emotional compensation offerings available to them. Communicate them widely in internal communication channels and encourage managers to highlight programs in check-ins, team meetings, and performance management discussions. Invite employees to ask questions and answer them promptly.
Step 5: Regularly measure programs
It may take some time for certain emotional compensation initiatives to have an impact, but be sure to regularly assess participation levels and get employee feedback on the quality of the programs. This effort will help ensure the company is meeting employees’ needs and using its resources effectively.
HR tip
Before committing significant time and resources to major emotional compensation initiatives, try testing them on a smaller scale. Consider implementing pilot programs for certain teams or departments to assess their effectiveness and popularity. Taking this step can help you make any necessary adjustments before rolling out any initiative company-wide.
FAQ
An example of emotional compensation is offering a company wellness program that features a range of physical fitness and mental health initiatives. These may include gym classes, stress reduction workshops, and counseling services.
An emotional salary refers to non-financial benefits provided by employers, such as flexible work hours, recognition programs, and wellness initiatives, that contribute to employee satisfaction and wellbeing.