Decentralized Management
What is decentralized management?
Decentralized management is an organizational structure where decision-making authority is distributed throughout an organization, rather than only at the top. Unlike centralized management, it allows all managers to make strategic and operational decisions on their individual teams and projects.
Decentralized management still involves necessary checks and balances (e.g., compliance procedures and risk management) but enables greater agility and responsiveness when change is needed.
Key features of decentralized management
The main components of decentralized management include:
- Authority at multiple levels: Decision-making power is shared across departments, teams, or individuals rather than a small group of senior leaders.
- Greater flexibility: Decentralized management enables agility and responsiveness to changing trends and markets.
- Local autonomy: Teams or regional departments can make decisions tailored to their specific needs without prior executive management approval.
- Flatter structure: Decentralized management has a flat organizational structure with fewer hierarchical layers, facilitating greater employee autonomy.
- Collaborative culture: Teamwork and diverse perspectives are necessary for this structure to be effective.
- Focus on empowerment: Employees at different levels are trusted and supported to act independently within their roles, empowering them to innovate and take action.
- Communication and collaboration: Open and frequent communication across departments, alongside less top-down communication, drives collaboration.
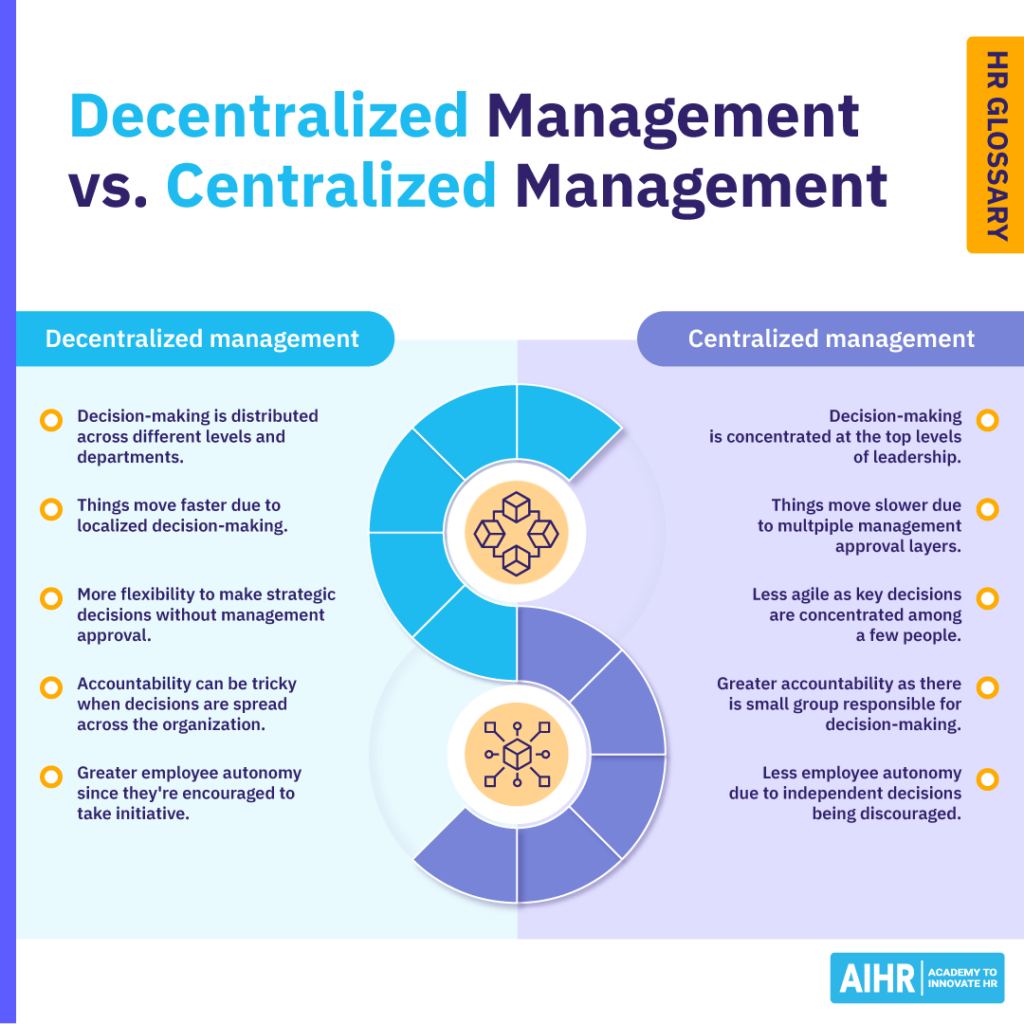
Decentralized vs. centralized management
Decision-making
Distributed across different levels and departments
Concentrated at top leadership levels
Speed of decisions
Faster due to localized decision-making
Often slower due to multiple management approval layers
Flexibility
More flexibility to make strategic decisions without needing management approval
Less flexible, as only a few senior managers can make key decisions
Accountability
Trickier, as decisions are spread among more people across the organization
Greater accountability due to a small group being responsible for major decisions
Employee autonomy
Greater employee autonomy since employees are encouraged to take initiative
Less employee autonomy due to independent decisions being discouraged
3 decentralized management examples
Here are some real-life examples of organizations that use decentralized management:
1. Amazon
Amazon enables decentralized decision-making through its “two-pizza team” approach (teams not big enough to eat two pizzas). These small teams of under 10 people are largely autonomous and work closely on specific tasks or projects. This concept empowers individual teams to make decisions quickly without needing approval from higher-ups.
2. Johnson & Johnson
Johnson & Johnson and its subsidiaries operate under a decentralized structure, with each business segment (consumer goods, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices) having its own management and decision-making authority. This gives the company the agility to adapt its products to meet the needs of different markets and consumer groups.
3. Spotify
Spotify has Squads, Tribes, Chapters, and Guilds through which multi-disciplinary, product-focused teams work mostly autonomously. Though there are product owners and project leads within various working groups, Spotify employees are expected to work closely without constant managerial direction. This enables better responsiveness to market forces.
Learn how to help your organization successfully manage its talent
To maintain a productive, satisfied workforce under any management style, your organization must be able to align workforce needs with management goals, foster employee engagement, and ensure policy compliance.
In AIHR’s Talent Management and Succession Planning Certificate Program, you’ll learn to systematically implement talent management strategies that support business sustainability and create an environment for talent to thrive.
Advantages and disadvantages of decentralized management
A decentralized management structure has certain advantages and disadvantages, such as:
Advantages
- Greater innovation and creativity: Decentralized organizations empower employees at different levels to take initiative, share ideas, and provide feedback and suggestions that make innovation easier.
- Faster decision-making in localized contexts: Managers in decentralized organizations can localize overall strategic direction to suit specific markets, consumer needs, and other business needs without management approval.
- Improved employee engagement: The opportunity to contribute ideas and take initiative can boost motivation, engagement, and job satisfaction. This can improve a company’s employer brand, attracting and retaining more talent.
- Reduced bottleneck effect: Unlike centralized systems, decentralized organizations don’t usually experience delays from awaiting executive approval. This allows managers and project leaders to make critical decisions more quickly.
- Leadership skills across multiple organizational levels: Allowing employees and their managers to make decisions without executive approval can help their leadership skills in their teams and projects.
Disadvantages
- Risk of inconsistent decision-making: More people involved in the decision-making process may lead to a lack of uniformity and alignment among different teams. This could result in inconsistencies and inefficiencies.
- Reduced oversight: The lack of central oversight and control may pose a legal, financial, or safety risk to some organizations, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals, finance, and healthcare.
- High dependence on employee competence: A decentralized organization requires employees to be motivated and competent. It also relies on a high level of trust in its workforce to be able to make critical decisions.
- Requires a robust communication approach: Decentralized management needs an especially clear, strategic communication approach to avoid misalignment and inconsistencies. Otherwise, teams may be confused over organizational goals.
- Difficult to implement in entrenched hierarchies: A company looking to transition from a centralized to a decentralized system may encounter resistance from senior management reluctant to relinquish control or oversight.
HR tip
An effective decentralized management structure depends heavily on developing leadership skills at all levels. Instead of focusing only on mid- and lower-level managers, expand your leadership training to accommodate all levels. Tailor workshops and training sessions to suit managers’ needs and improve their decision-making, problem-solving, communication, critical thinking, and collaboration skills.
FAQ
Decentralized management is an organizational structure in which decision-making authority is distributed across various levels rather than concentrated at the top. This approach allows departments, teams, or regional offices to make decisions independently, fostering flexibility, faster responses, and greater employee involvement.
Centralized management keeps decision-making at the top, ensuring control and consistency but slowing responses. Decentralized management spreads authority across levels, allowing faster decisions and flexibility but with potential inconsistencies.