Workforce Automation
What is workforce automation?
Workforce automation is the use of technology to simplify various tasks and processes within an organization. This can involve a wide range of activities across various industries aimed at improving efficiency, reducing costs, and streamlining processes. Implementing automation in the workforce allows businesses to enhance productivity while freeing up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
HR professionals play an essential role in identifying opportunities for workforce automation, selecting appropriate tools, and facilitating a smooth transition for employees, ensuring they can focus on more dynamic and impactful work.
How workforce automation works
- Workforce automation replaces manual tasks with automated systems
- It uses software and AI to handle repetitive processes without human intervention
- It helps employees focus on more strategic and high-value activities
- It reduces the risk of human error by ensuring consistency and accuracy
- It simplifies workflows and optimizes business processes for better efficiency.
Examples of workforce automation
Although the types of workforce automation can vary in organizations, here are a few common examples:
- Chatbots and virtual assistants: Tools like chatbots and virtual assistants use AI to handle customer inquiries and support issues. They can answer FAQs, process orders, and route complex issues to human agents.
- Recruiting: Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) automate tasks like job posting, résumé screening, interview scheduling, and candidate communication. They help streamline the recruitment process, improving the efficiency and accuracy of candidate selection.
- Email marketing: Platforms like Mailchimp and HubSpot automate email campaigns, segment audiences, and personalize messages, saving time and enhancing marketing efforts.
- Customer relationship management (CRM): CRM tools like Salesforce automates sales pipelines, customer communications, and data management, helping businesses improve customer relationships and sales efficiency.
- Payroll processing: Payroll automation tools manage employee salaries, tax deductions, and benefits calculations, ensuring timely and accurate payments with minimal manual input.
- Agricultural automation: Farms use automated machinery to plant, water, and harvest crops. Drones are also employed to monitor crop health from above, providing data that helps farmers make better decisions about crop management.
- Retail kiosks: Automated kiosks in retail stores allow customers to check out without having to interact with cashiers. These kiosks can scan items, process payments, and even provide customer assistance via touchscreens or voice responses.
Did you know?
Contrary to popular belief, the future of work is not expected to be fully automated. In reality, technology will likely complement human efforts rather than replace them.
As reported by the International Federation of Robotics, very few jobs – less than 10% – are fully automatable. Instead, robots primarily take over tedious, repetitive tasks, allowing human employees to devote more time to more complex, significant aspects of their work.
Advantages of workforce automation
Workforce automation can offer significant benefits, such as:
- Increased productivity: Automation allows for tasks to be completed more efficiently and quickly, leading to higher productivity levels. This efficiency can result in quicker delivery times and cost savings.
- Reduced errors: Automated processes are less prone to errors compared to manual operations, enhancing the accuracy of tasks such as data entry, invoicing, and inventory management.
- Better resource utilization: Automation enables businesses to allocate their employees to more critical tasks that require human intelligence, creativity, and emotional understanding, thereby putting their workforce’s unique skills to better use.
- Safety improvements: Automation can handle hazardous or physically demanding tasks that may pose risks to human workers. By delegating these tasks to machines, businesses can improve workplace safety and reduce the occurrence of accidents and injuries.
Optimize HR processes with workforce automation
Workforce automation streamlines operations, enhances efficiency, and frees employees to focus on strategic work. From AI-powered chatbots to automated payroll systems, HR plays a critical role in selecting and implementing these tools effectively.
In AIHR’s Digital HR 2.0 Certificate Program, learn how to integrate automation into HR processes, drive digital transformation, and future-proof your organization’s workforce.
Disadvantages of workforce automation
Despite the benefits, there are some disadvantages to consider, including:
- Training involved: Using and adapting to automated technology and workflows often requires training. HR teams may need to devote time and resources to training employees on how to use workforce automation software or invest in upskilling initiatives to help them better collaborate with automation tools.
- Initial costs and investment: Although automation can save money over time, the initial setup, integration, and maintenance costs can be prohibitively high, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Dependency on technology: Over-reliance on technology can make businesses vulnerable to technical failures or cybersecurity attacks. Any disruption in the automated systems can lead to significant operational delays or losses.
- Reduced human interaction: Depending on the type of workforce automation implemented, less human interaction among colleagues, customers, and clients may occur. This change may negatively impact team dynamics and customer relationships.
Workforce automation software
Here are some examples of workforce automation software:
| Customer service automation | • Zendesk: Uses AI and automation to streamline customer service processes, including ticketing and customer engagement. • Freshdesk: Provides automation features for managing tickets, dispatching them based on workflows, and using chatbots for initial customer interactions. |
| Marketing automation | • HubSpot: Offers an entire suite of essential marketing tools for email marketing, social media scheduling, and marketing analytics. • Mailchimp: Primarily focuses on email marketing automation, allowing users to create targeted email campaigns, subscriber list management, and campaign tracking. |
| Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) | • Workday: A cloud-based HRIS platform that automates key tasks like payroll processing, managing employee benefits, onboarding, and performance management. • SAP SuccessFactors: A comprehensive cloud-based suite that offers tools for payroll automation, time tracking, recruiting, onboarding, and enhancing employee experience and engagement. |
| Payroll automation | • ADP: Known for its payroll services, it also provides comprehensive global human capital management (HCM) solutions. • Paychex: Offers payroll and HR solutions, including payroll processing, retirement services, insurance, and fully integrated HR solutions. |
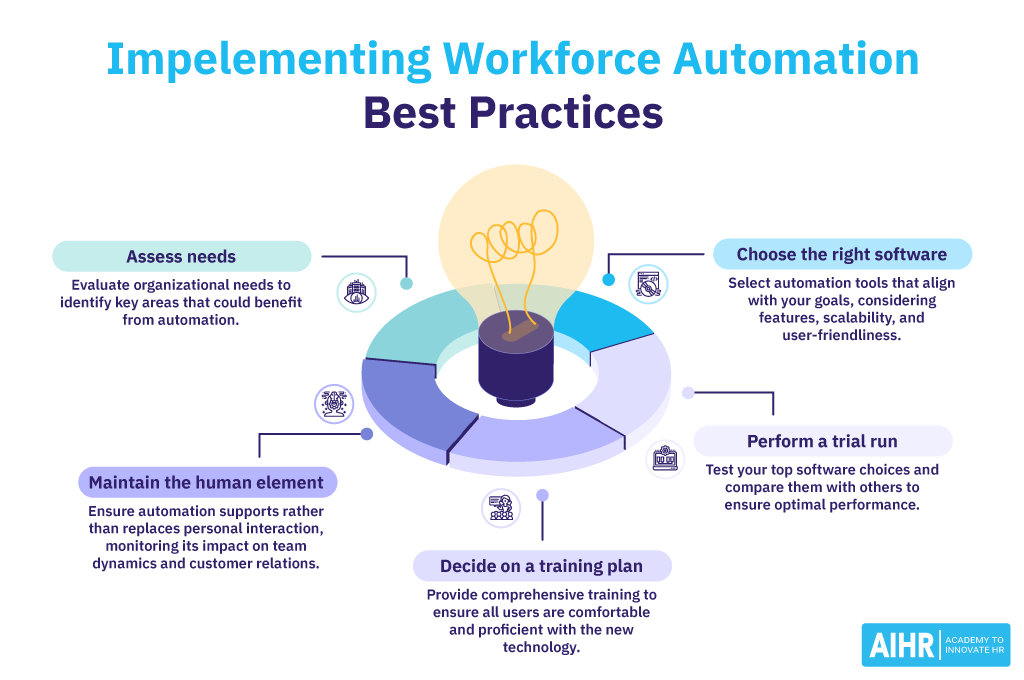
Tips for implementing automation in your workforce
Follow these best practices to implement workforce automation effectively:
- Assess your organization’s needs: Before implementing any workforce management automation solutions, assess the organization’s needs thoroughly. Identify which processes are time-consuming or error-prone and could benefit from automation. This could include tasks like payroll, employee onboarding, performance reviews, or scheduling.
- Choose the right software: The next step is to select the right automation tools that align with organizational goals. This involves evaluating different technologies for their features, scalability, compatibility with existing systems, and user-friendliness.
- Perform a trial run: Once you’ve narrowed your choices for workforce automation software, compare it with others. Make use of any free trials available so you are sure your chosen solution performs well compared to others on the market before investing in one.
- Decide on a training plan: Provide comprehensive training and support to ensure all users are comfortable with and proficient in the new technology. This might include hands-on workshops, online tutorials, and steady support channels to address any questions or issues that arise.
- Don’t forget the human element: Automation in the workforce shouldn’t replace personal interaction. It’s crucial to maintain connections for complex situations that need a human touch. Regularly monitor any automation to ensure there’s no negative impact on team dynamics, customer service, or client relationships.
When choosing automation software, think long-term. Assess its scalability and adaptability to support your organization’s future workforce needs. Choose workforce automation solutions that not only integrate into your existing HR systems but also provide ongoing updates to keep up with emerging technologies, such as cloud-based solutions. Taking these steps will help you avoid costly software changes.
HR tip
To truly benefit from workforce automation, track key metrics like processing times, error rates, cost reductions, and employee productivity, then share the results to showcase impact and identify areas for improvement.
The future of AI and automation in the workforce
The future of automation will transform how businesses operate, improving efficiency and creating new opportunities. Companies will increasingly rely on AI workforce automation to handle repetitive tasks, analyze data, and support decision-making.
While automation will streamline operations across HR, finance, and customer service, it won’t replace human involvement. Instead, it will enhance human capabilities, allowing employees to focus on complex, strategic work. For HR professionals, this shift means leveraging AI tools to improve talent management and employee engagement while ensuring staff are equipped to thrive alongside automation.