Relational Leadership
What is relational leadership?
Relational leadership is a leadership style that focuses on the importance of relationships in guiding and motivating individuals or teams toward achieving goals. It emphasizes building trust, fostering collaboration, and encouraging open communication among team members.
Rather than focusing solely on task execution or hierarchical control, relational leaders prioritize creating an environment where everyone feels valued, heard, and supported.
The relational leadership theory suggests that effective leadership is inherently relational, with the quality of relationships between leaders and followers being central to leadership success.
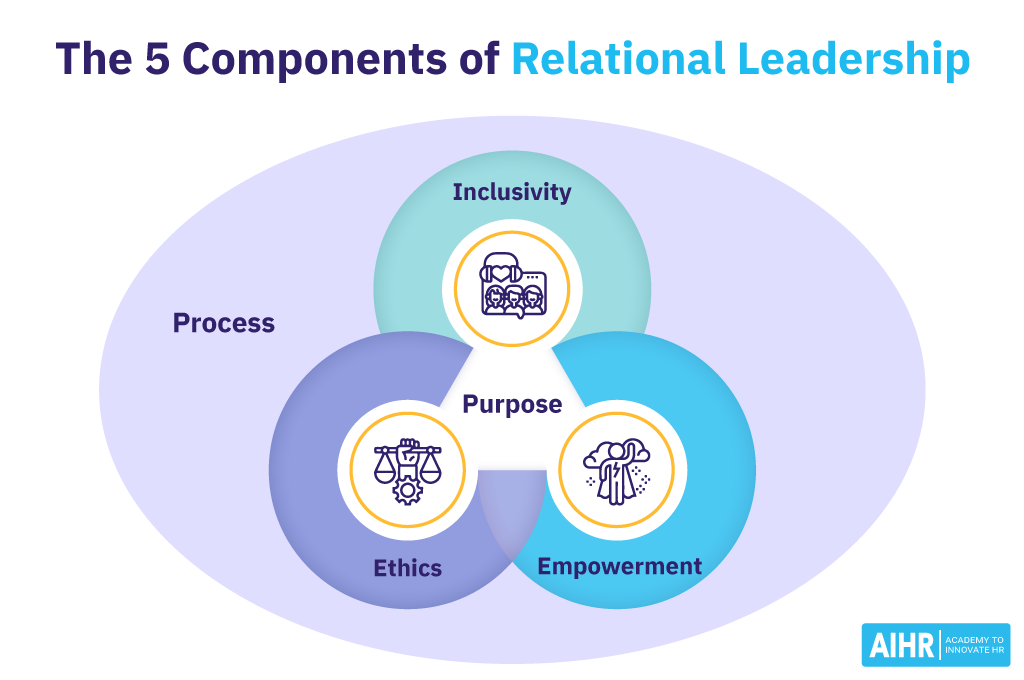
5 components of the relational leadership model
The relational theory of leadership comprises five core components, each playing a crucial role in fostering effective leadership and organizational success:
- Ethics: Ethical leadership is at the heart of relational leadership. It involves making decisions based on fairness, honesty, and integrity. Relational leaders prioritize ethical considerations in all aspects of their leadership, ensuring their and their organization’s actions reflect a commitment to moral principles.
- Inclusivity: Relational leaders strive for inclusivity, making concerted efforts to ensure everyone, regardless of background or identity, feels valued and included. This component emphasizes the importance of diversity and equality within the organization, fostering an environment where all voices are heard and respected.
- Process orientation: Unlike leadership styles focusing solely on outcomes, relational leadership strongly emphasizes the processes leading to those outcomes. This involves focusing on how decisions are made, how tasks are accomplished, and how people work together. Process orientation ensures the journey to achieving goals is just as valued as the goals.
- Empowerment: Empowering team members is a crucial aspect of relational leadership. This involves delegating authority, encouraging autonomy, and providing the resources and support team members need to succeed. By empowering their team, relational leaders foster a sense of ownership and accountability among employees.
- Purpose: A clear and compelling purpose is essential in relational leadership. Relational leaders articulate a vision that resonates with their team, aligning individual and organizational goals. This shared purpose motivates and unites team members, driving collective action towards achieving common objectives.
Relational leadership examples
Here are some examples of relational leadership style in action:
- Team collaboration: A relational leader encourages open communication and teamwork. For instance, in a project team, they might facilitate brainstorming sessions, ensuring everyone has a voice and their ideas are valued.
- Mentorship and support: A relational leader acts as a mentor to their team members. For example, a manager might take time to understand an employee’s career goals, providing guidance and support to help them develop professionally.
- Empowerment and delegation: Rather than micromanaging, a relational leader empowers their team by delegating tasks and giving them the autonomy to make decisions. For instance, a leader might entrust a team member with a major project, providing them with the necessary resources and guidance while allowing them to take ownership.
- Conflict resolution: When conflicts arise, a relational leader takes a proactive role in resolving them. For example, if two employees have a disagreement, the leader will listen to both sides, mediate, and try their best to find a solution that respects both perspectives.
Benefits of relational leadership
Here are some key benefits of relational leadership:
- Enhanced team collaboration and cohesion: Relational leadership fosters an environment of open communication and mutual respect, which improves team collaboration.
- Better conflict resolution: Relational leaders are skilled at navigating disagreements to preserve relationships and find mutually beneficial solutions.
- Higher levels of trust and respect among team members: Trust is a critical component of effective leadership. Relational leaders build trust by being transparent, showing integrity, and demonstrating genuine care for their team members.
- Greater adaptability and resilience in the face of change: Organizations led by relational leaders tend to be more adaptable and resilient. These leaders value input from their team and are more likely to embrace change and innovation as they understand the importance of evolving to meet new challenges.
Transactional vs. relational leadership
Transactional and relational leadership differ in how they influence and engage employees.
Focus
Task completion, efficiency, and achieving specific goals.
Building strong relationships, trust, and collaboration.
Leader-follower dynamics
The leader is in control and gives directives; follower compliance is expected.
Leadership is a mutual process; both leader and followers influence each other.
Leadership style
Authoritative, task-oriented, and control-driven.
Supportive, relationship-oriented, and development-focused.
Example
A manager rewarding employees for meeting sales targets or meting out penalties those who underperform.
A leader mentoring their team, fostering teamwork, and encouraging professional development.
Tips for implementing relational leadership
Here are six helpful tips for cultivating a relational leadership style within your organization:
- Lead by example: Leading by example is critical to establishing a culture of trust, respect, and integrity. When leaders consistently demonstrate the behaviors and values they wish to see in their team, it sets a powerful precedent. This includes showing vulnerability, admitting mistakes, and treating failures as learning opportunities.
- Get to know your employees: Investing time to understand each team member’s strengths, weaknesses, aspirations, and personal interests signifies a genuine investment in their wellbeing and professional development. This can be achieved through regular one-on-one meetings, informal check-ins, and showing interest in their life outside of work.
- Support professional and personal growth: Investing in employees’ professional development not only enhances their skills and career prospects but also benefits the organization by promoting a culture of ongoing learning and adaptability. Offering training programs, mentorship opportunities, and support for further education are key strategies.
- Develop peer coaching circles: Peer coaching circles offer a platform for employees to share skills, knowledge, and experiences in a supportive and structured environment. These circles facilitate talent development, problem-solving, and the strengthening of interpersonal relationships across the organization.
HR tip
To cultivate a strong relational leadership culture, prioritize active listening in everyday interactions. Employees feel valued when their input is genuinely heard and considered. Simple actions like maintaining eye contact, paraphrasing key points, and following up on conversations can strengthen trust and engagement across your team.
FAQ
The five components of a relational leadership model are:
• Purpose: A clear and shared vision that guides the team.
• Ethics: Commitment to ethical practices and integrity in leadership.
• Empowerment: Encouraging team members to take initiative and grow.
• Communication: Open, honest two-way communication.
• Inclusivity: Creating a culture where all voices are valued and included.
An example of relational leadership is when a manager actively mentors their team, providing continuous feedback, recognizing each member’s contributions, and fostering an environment where everyone feels valued and motivated to contribute their best.
Transformational leadership focuses on inspiring and motivating followers to achieve higher performance and embrace change, often driven by a strong vision. Relational leadership, on the other hand, prioritizes building trust, collaboration, and strong interpersonal relationships to create a supportive and inclusive environment. While transformational leadership drives innovation and change, relational leadership fosters connection and teamwork.