Formalization
Formalization meaning
Formalization is the degree to which fixed rules and procedures dictate how an organization’s employees should behave. It is one of the key dimensions in organizational design, as it helps the organization provide a more predictable product or service.
Examples of formalization
Which restaurant do you expect to be more formalized: a family-owned casual dining restaurant or a Michelin-starred restaurant? The former likely has a few hygiene rules dictated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). However, the latter would have extensive rules on greeting customers, food presentation, cleaning tables, and even how to present the bill. The Michelin-starred restaurant might have detailed instructions on the precise placement of utensils, the exact sequence in which courses are served, and a strict dress code for staff. Even the way the bill is presented to the customer might follow a specific protocol to ensure a consistent and high-end experience.
Other examples of formalization include job descriptions, clearly defined responsibilities, behavioral norms (like how to request days off), the SOP for informing the manager when you need a sick day, internal bookkeeping norms, and so on. In a corporate setting, job descriptions might include not just the tasks an employee is expected to perform but also the metrics by which their performance will be judged, the expected timeline for task completion, and the exact process for reporting progress. Behavioral norms in a highly formalized organization could include guidelines for how to dress, how to address colleagues and superiors, and even how to decorate one’s workspace.
Why is formalization important in an organization?
Formalization is important for several reasons, including:
- Consistency and standardization: Formalization ensures that processes, procedures, and policies are standardized across the organization. This leads to consistent outcomes and reduces variability, which is crucial for maintaining quality and reliability.
- Efficiency and productivity: Well-defined procedures streamline operations, reduce redundancy, and improve efficiency. Employees can work more effectively when they have clear instructions and know the best practices to follow.
- Training and onboarding: Formalized processes and procedures are essential for training new employees. They provide a reference point for learning and ensure that new hires can quickly adapt to their roles and perform tasks accurately.
- Accountability: Formalization establishes clear guidelines and standards, making it easier to hold individuals and teams accountable for their actions. It provides a framework for evaluating performance and ensuring compliance with company policies.
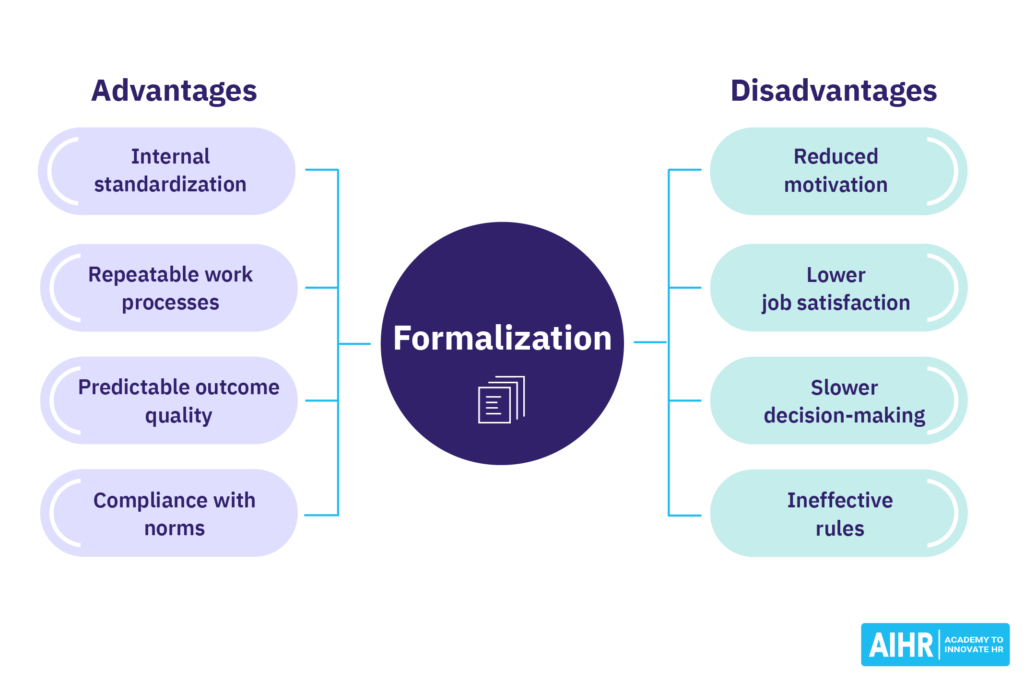
Advantages of formalization
Formalizing rules offers many benefits for an organization, such as:
- Internal standardization: Rules enable the creation of standards. A common safety standard is to hold the handrail when climbing a flight of stairs on an oil rig. With this rule, you’re less likely to be severely injured or die if you slip.
- Repeatable work processes: Formalization helps establish repeatable work processes. This means two machine operators who never interacted with each other can do the exact same job without any inconsistencies in their output. This makes roles replaceable and removes risk for the organization.
- Predictable product or service quality: Formalization results in higher-quality products or services. A Michelin-starred restaurant can consistently offer an exceptional dining experience because it follows strict standards and procedures to the letter.
- Compliance with external norms. Some products must comply with an external norm. For instance, all electrical equipment in Europe must be able to work at 207 to 253 volts. Otherwise, their sale is not permitted. The same concept applies to accounting standards and labor regulations.
Each of these reasons boils down to consistency and control. The rules allow an employer or manager to achieve exactly what they aim to, simply because everyone follows the rules.
Disadvantages of formalization
Excessive formalization also has drawbacks, including:
- Reduced motivation: Rules reduce worker autonomy, leading to lower motivation. This also means a highly formalized work environment is not for everyone.
- Less innovation: A work environment reliant on rules has little room for innovation, which may result in lower job satisfaction.
- Slow decision-making: Formalization standardizes the decision-making processes so that decisions must first travel through the organizational hierarchy, slowing them down and making the organization less agile.
- Ineffective rules: Sometimes, you can help a customer better by breaking a rule. Let’s say they come to your shop at closing time, and the rule is not to entertain customers within 10 minutes of closing time, but you help them anyway. Technically, you’ve broken a rule but have helped a customer and made them happy. They may even give the shop a good review and specifically mention your good service, benefiting you and the business.
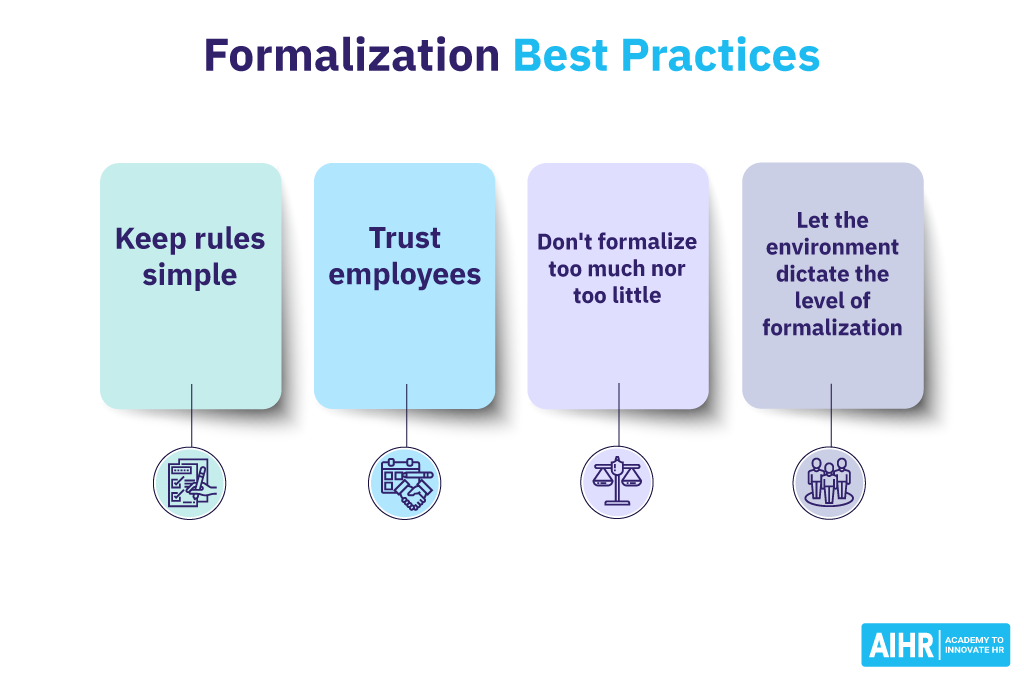
Formalization best practices
Implementing rules and processes works well as long as organizations apply them sensibly. Here are four best practices for formalization:
- Create simple rules: Keep rules as simple as possible. Complex rules are harder to follow and, thus, less effective. Netflix’s expense policy is summarized in one sentence: “Act in the company’s best interest.” Based on that, the company trusts everyone to practice good judgment. This is a much more effective rule than a 10-page document about which expenses are allowed or not allowed.
- Keep the onus on the employee: This is in line with the Netflix example: don’t overprescribe. Rules allow for control, but trusting people to use their best judgment is equally important. If you create rules because you don’t trust employees, you are not solving the right problem.
- Formalization is a balancing act. The degree of formalization is an inverted U-curve. Insufficient formalization will bring chaos, while excessive formalization will slow things down. Always aim for an optimum balance between too many and too few rules.
- Determine what level of formalization fits your environment: Optimum formalization depends on a number of factors. In her work, Professor Kathleen Eisenhardt mentions the following factors:
- Uncertainty: When market uncertainty is high, stick to lower formalization because the market is likely to change and evolve, and rules will slow down decision-making. This is why large, established companies often don’t succeed in new markets. In low-uncertainty markets, higher formalization is beneficial, as the market is predictable.
- Organizational newness: Small emerging organizations often have very little formalization. The most successful small entrepreneurial organizations are more structured than their peers, enabling them to outperform their competitors. If this is your organization, err on the side of structure.
FAQ
Formalization refers to the extent to which rules, procedures, and norms are standardized and explicitly defined within an organization. It involves the documentation and enforcement of policies, guidelines, and workflows to ensure consistent and predictable behavior among employees.
Formalization in management refers to the process of creating and implementing standardized procedures, policies, and rules within an organization. It ensures consistency, clear communication, accountability, efficiency, and compliance, facilitating smooth operations and helping the organization achieve its goals.
An example of formalization is a company’s employee handbook. This handbook typically includes detailed policies on attendance, dress code, performance evaluations, grievance procedures, and disciplinary actions. By documenting these rules and procedures, the company ensures that all employees understand and adhere to consistent standards and practices.
Organizations that operate in highly regulated industries, such as finance, healthcare, or manufacturing, are most likely to have a high degree of formalization. These industries require strict adherence to regulations and standards, necessitating comprehensive documentation and standardized procedures to ensure compliance and maintain quality and safety.