Coaching Leadership
What is coaching leadership?
Coaching leadership is a management style that focuses on developing and empowering employees by helping them improve their skills, knowledge, and overall performance. Leaders who adopt this approach act as coaches, guiding their team members through constructive feedback, active listening, and offering support to help them achieve their potential.
Instead of simply directing or managing tasks, coaching leaders work to build trust and encourage self-improvement. They help individuals set goals, identify strengths and areas for growth, and provide regular feedback to foster development.

Characteristics of the coaching leadership style
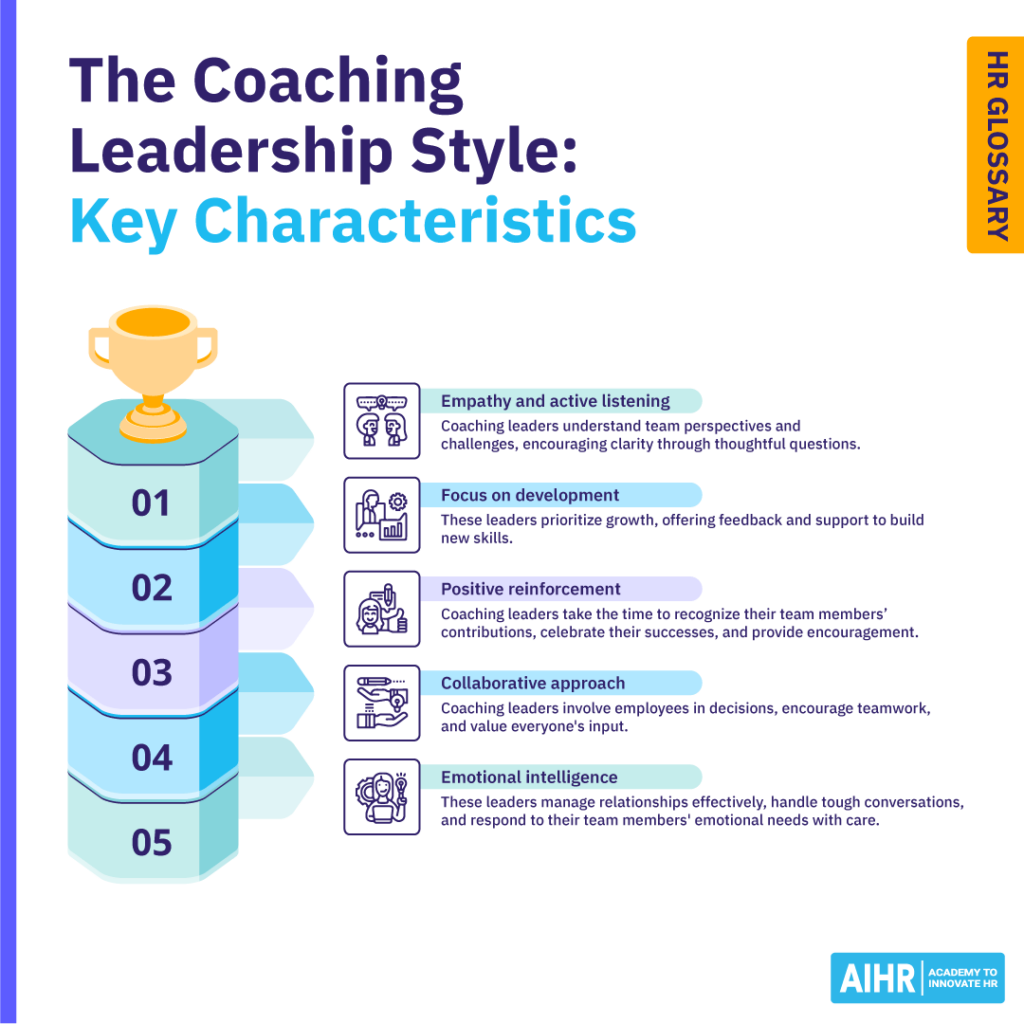
The coaching leadership style is defined by several key characteristics that emphasize development, collaboration, and trust. Here are some of its main traits:
- Empathy and active listening: Coaching leaders take the time to truly understand their team members’ perspectives, challenges, and goals. They listen carefully, asking insightful questions to help others reflect and gain clarity.
- Focus on development: Coaching leaders prioritize their employees’ personal and professional growth rather than just managing day-to-day tasks. They provide constructive feedback, suggest areas for improvement, and offer support to help individuals develop new skills.
- Positive reinforcement: Coaching leaders take the time to recognize their team members’ contributions, celebrate their successes, and provide encouragement. They look for reasons to praise and promote their teams within the organization.
- Collaborative approach: These leaders view their role as a partner to their team. They involve employees in decision-making, encourage teamwork, and value input from everyone.
- Emotional intelligence: A high level of emotional intelligence is crucial for coaching leaders, as it helps them manage relationships, navigate difficult conversations, and respond appropriately to team members’ emotional needs.
Coaching leadership examples
To fully understand this style, it’s helpful to explore key coaching techniques and see how they work in real-world scenarios. Here are some examples of coaching leadership in action:
- One-on-one development plans: Coaching leaders work closely with individual team members to set personalized goals based on their strengths and areas for growth. Together, they create actionable, measurable plans focused on both personal and professional development. Leaders provide their team members with the resources and support necessary to achieve these goals.
- Skill-building workshops: A key coaching leadership strategy is offering opportunities for team members to learn new skills. This may involve organizing workshops, sending team members to specialized conferences, or bringing in instructors for hands-on training. Leaders follow up to ensure team members can apply their new skills in the workplace.
- Mentorship programs: Coaching leader techniques can also include acting as a mentor to others or pairing team members with more seasoned teammates. This increases knowledge transfer while modeling preferred behaviors and processes. Mentors can offer advice, insight, and networking connections to help less experienced team members advance in their careers.
- Progress check-ins: Coaching leaders regularly check in with their team members to discuss progress, provide feedback, and address any challenges. These check-ins are not only for offering constructive feedback but also for celebrating team successes and keeping motivation high.
Drive employee development with effective leadership
Effective leadership can drive employee development and aid in succession planning. To ensure this, you must create and implement strategies that align employee development with organizational goals, while fostering continuous learning and growth.
In AIHR’s Talent Management and Succession Planning Certificate Program, you’ll learn to align leadership practices with workplace culture, and facilitate talent mobility.
Here are some good examples of coaching leaders:
- Satya Nadella, Chairman and CEO of Microsoft: In the last decade, Nadella has transformed Microsoft using coaching leadership skills. His focus on creating a culture of learning and diversity has helped the company thrive as an innovator in the tech space.
- Ken Blanchard, author and leadership expert: A well-known expert in leadership development, Blanchard has promoted the ideals of coaching leadership methods through over 70 published books and multiple public speaking events and programs. His work has inspired others to build more productive relationships and become better communicators.
- Indra Nooyi, author and former Chairwoman and CEO of PepsiCo: Serving PepsiCo from 2006 to 2019, Nooyi was the first woman of color and the immigrant to head a Fortune 500 company in the USA. Her coaching leadership style was based on empowering team members to be accountable for their work and professional development.
Coaching leadership style: Pros and cons
Let’s explore the potential pros and cons of the coaching leadership style:
The pros
- Enhanced employee engagement: Coaching leaders can increase employee engagement by promoting autonomy, which improves their sense of work ownership. In general, this leads to job satisfaction and organizational engagement.
- Skill development boosted: Coaching leaders who invest time in their team members’ professional growth reap the rewards of greater innovation and creativity. Transferring knowledge through mentoring and training opportunities accelerates their ability to handle whatever the future brings.
- Improved problem-solving: Coaching leaders can facilitate problem-solving by encouraging their team members to think about solutions, and giving them constructive feedback
- Stronger team relationships: Building trust as a coaching leader helps create an inclusive environment where people can develop stronger relationships. Active listening and open communication promote organizational delayering, increasing confidence and sharing.
The cons
- Time-intensive: This leadership style demands a significant amount of time and effort from leaders. Carving out this time can be challenging, especially in agile-based work environments.
- Potential for micromanagement: If coaching leadership is not monitored, it can lead to micromanagement of team members. Whether intentional or not, this will damage team performance and engagement.
- Strong coaching skills required: For this style to be effective, leaders need a strong grasp of coaching principles and a commitment to continually refining their skills.
- Not suitable for every situation: In high-pressure or crisis scenarios, coaching leadership might feel out of place or inefficient, as it emphasizes collaboration and personal development over immediate results.
When is coaching leadership effective?
Coaching leadership is highly effective in situations where guidance is needed, but individual autonomy is respected. It works particularly well in the following scenarios:
- New and growing teams: A newly formed or rapidly growing team provides the perfect opportunity for coaching leadership skills. Coaching leaders can help integrate new team members into the organization’s structure and culture. They can also help team members find their place as they discover their talents, which builds confidence.
- Future leaders: Leadership coaching also supports the professional development of high-potential team members who may become future leaders. Modeling coaching leadership reinforces the ideals of leadership while guiding others toward success, allowing people to reach their full potential.
- Cultural transformation: Coaching leadership plays a key role in improving organizational culture. It promotes better communication, encourages positive behaviors, and fosters tolerance and inclusion, helping drive meaningful cultural change.
- Remote and hybrid team building: With the rise of remote and hybrid team management, coaching leaders are challenged to maintain strong teams by using their coaching skills. They can address these challenges by regularly hosting virtual meetings to keep their teams engaged and connected.
HR tip
Encourage managers to adopt coaching leadership with tools like training and mentorship. Regular check-ins and skill-building sessions can boost engagement, improve collaboration, and foster a culture of growth across teams.