Autocratic Leadership
What is autocratic leadership?
Autocratic leadership refers to a management style in which decision-making power is concentrated in the hands of a single leader without input from group members.
This leader makes decisions based solely on their judgment and perspectives, typically without considering the opinions or suggestions of others. Such leaders enforce strict obedience and expect their directives to be executed without dissent. This leadership style is most recognized for its direct, no-nonsense approach to management and governance, and can be effective in certain professional scenarios where ambiguity is considered a liability.
While authoritative leadership also involves clear, firm direction, it is combined with support and guidance, encouraging input and fostering a positive, collaborative environment.

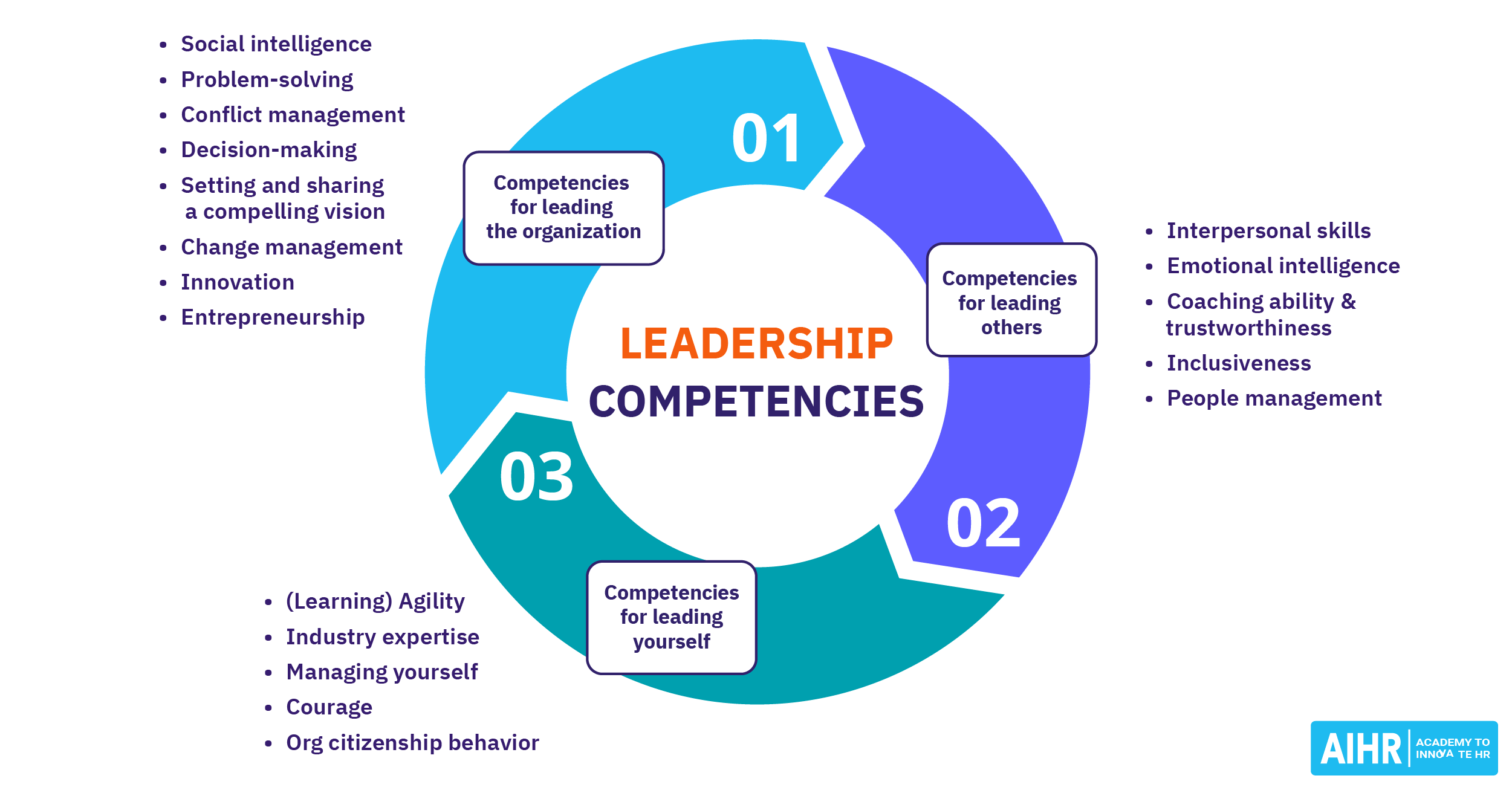
Characteristics of the autocratic leadership style
Autocratic leadership is characterized by a high level of control and decision-making authority held by the leader, with minimal input from subordinates or team members. Here are some key characteristics:
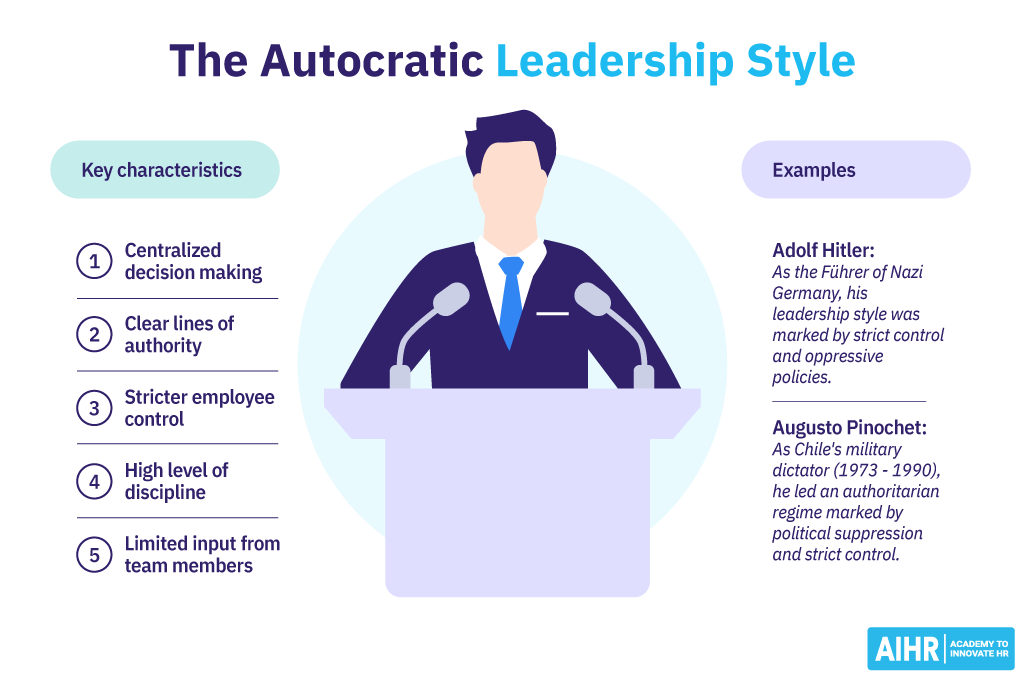
- Centralized decision-making: The leader holds all the decision-making power. They make decisions independently, without consulting their team members or seeking their input.
- Clear lines of authority: Autocratic leaders establish clear, distinct lines of authority. They are at the top, and their commands flow downward. There is no ambiguity about who is in charge and who makes the decisions.
- Stricter control: Autocratic leaders maintain strict control over their team members. They closely monitor their work and may dictate how tasks should be completed without allowing much flexibility or autonomy.
- High level of discipline: Autocratic leadership fosters an environment where discipline is paramount. Leaders expect strict adherence to rules and procedures to enhance operational efficiency and reduce errors, especially in settings where precision is vital.
- Limited input from team members: Feedback or input from team members is typically kept to a minimum. The focus is on obedience and execution, not collaborative problem-solving. This may be effective when too many opinions might complicate straightforward tasks.
Autocratic leadership examples
Autocratic leadership has been prevalent across various sectors, including business and the military. Here are some notable autocratic leaders:
- Adolf Hitler: As the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945, Hitler’s intensely autocratic style of leadership relied solely on his vision and employed brutal methods to ensure compliance.
- Queen Elizabeth I: Her reign is famous for her autocratic rule, which allowed decisions to be made solely at her discretion. Yet, her leadership led to a period of English prosperity, the defeat of the Spanish Armada, and the flourishing of arts and culture.
- Napoleon Bonaparte: As the Emperor of France, Napoleon centralized all major decisions, requiring unquestioning obedience from his subordinates.
- Vladimir Putin: The President of Russia is described as autocratic because of his strong control over government, media, and public life in Russia and his centralized power structure that stifles opposition.
Pros and cons of autocratic leadership
Advantages
Here are some of the primary pros associated with this leadership style:
- Quick decision-making: The ability to make swift decisions without consultation can be useful in scenarios requiring quick action.
- Simplicity in operations: For large organizations or those with complex hierarchies, autocratic leadership can simplify command chains, making it easier to manage operations and enforce policies.
- Consistency and order: Autocratic leadership ensures work processes are consistently followed, leading to predictable outcomes and organizational stability.
- Optimal for routine tasks: This leadership style can thrive in operations where innovation is less critical than predictability and speed.
Disadvantages
While autocratic leadership can be practical in specific situations, it also has notable disadvantages that can impact team dynamics, innovation, and overall morale.
- Suppression of team innovation: Autocratic leadership can prevent the development of employees’ leadership skills and reduce opportunities for employees to take initiative or make meaningful contributions.
- Risk of high turnover rates: Employees who feel their opinions and expertise are consistently ignored may become dissatisfied, leading to higher turnover rates.
- Lower employee morale: The lack of involvement in decision-making processes can demotivate employees and reduce their job satisfaction.
- Reduced creativity: Centralized decision-making leaves little room for team members to contribute ideas or innovative solutions. This can suppress creativity and prevent the company from benefiting from diverse perspectives.
Autocratic vs. authoritarian vs. democratic vs. participative leadership
| Leadership style | Key characteristics | Decision-making process | Focus | Employee involvement |
| Autocratic leadership | Centralized control; leader makes all decisions without consulting subordinates | Leader-centric, no team input | Task completion and control | Minimal to none |
| Authoritarian leadership | Similar to autocratic but often harsher; focuses on obedience and strict adherence to rules | Leader-centric with rigid expectations | Enforcing rules and discipline | Minimal; expected to follow orders |
| Democratic leadership | Encourages group participation; leader seeks input but retains final decision-making authority. | Collaborative but leader-driven | Balancing task and team morale | High involvement in discussions |
| Participative leadership | Emphasizes collaboration; decisions are often made collectively or with significant team input. | Shared decision-making with the team | Team empowerment and shared goals | High; employees play an active role |
When to use an autocratic leadership style
An autocratic leadership style is best used in situations that require clear direction, fast decision-making, or strict compliance. It is particularly effective in the following scenarios:
- Crisis or emergency situations: When quick decisions are essential, such as during a natural disaster or safety-related incident, an autocratic leader can streamline the response process without delays from team input.
- Highly regulated or high-risk environments: Industries like healthcare, manufacturing, or construction often require adherence to strict protocols. An autocratic approach ensures compliance and minimizes risk.
- Inexperienced or untrained teams: If the team lacks the necessary skills or knowledge, providing clear, direct instructions through an autocratic style can prevent mistakes and maintain productivity.
- Meeting tight deadlines: When time is a critical factor, such as when delivering a project under extreme time pressure, this leadership style reduces decision-making time and ensures everyone stays on task.
- Military or law enforcement settings: These roles often demand immediate compliance and decisive leadership to achieve objectives or maintain safety.
- Maintaining order in large teams: Autocratic leadership helps establish structure and clear accountability in situations where managing a large group of people is challenging.
HR tip
HR managers dealing with autocratic leaders should prioritize establishing communication channels that enable team members to express their views and feel valued, even when their suggestions may not be adopted. This can help maintain morale and reduce turnover.
FAQ
An autocratic leader typically exhibits several defining traits:
– Decisiveness: The ability to make quick decisions independently.
– Authority: Commanding presence that encourages compliance.
– Control: Keeps tight control over all aspects of operations.
Adolf Hitler, Augusto Pinochet, and Napoleon Bonaparte are prominent autocratic leaders. Hitler led Nazi Germany, enforcing strict totalitarian control through the subjugation of Jewish populations. Pinochet ruled Chile through a military dictatorship marked by severe human rights violations. Napoleon, after his rise during the French Revolution, declared himself Emperor of France, effectively centralizing his power.
While effective in specific contexts, autocratic leadership can be detrimental as it often stifles creativity and reduces employee engagement. This lack of team involvement can hinder skill development and initiative, making organizations less adaptable to change and less competitive over time.